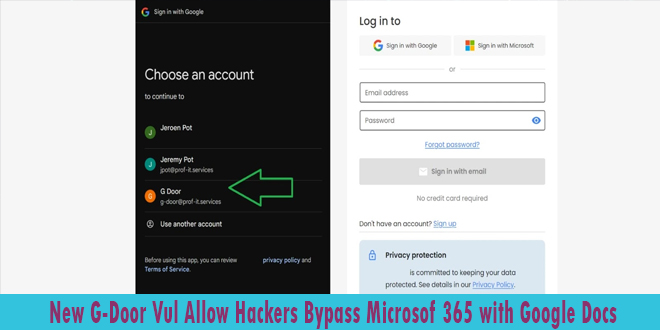
A newly discovered vulnerability called “G-Door” enables malicious actors to bypass Microsoft 365 security by exploiting unmanaged Google Docs accounts. This flaw poses a serious threat to organizations using Microsoft 365’s Conditional Access policies.
The G-Door vulnerability stems from the ability to create personal or workspace Google accounts using a company’s domain name. These unmanaged accounts can access third-party applications, bypassing Microsoft 365’s security measures.
G-Door Vulnerability Security Risks:
Circumventing Conditional Access: Users or attackers can create Google accounts using corporate email addresses, bypassing important security measures such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), device checks, and location restrictions.
Lack of Visibility: Activity from these unmanaged accounts isn’t logged in Microsoft 365 Admin Center, making it hard to respond to incidents and detect anomalies.
Sensitive information in Google Drive or Google Docs is not protected by corporate Data Loss Prevention (DLP) or Azure Information Protection (AIP) policies.
Persistent Access: When attackers gain control of a Microsoft 365 account, they can create a new Google identity, keeping access to third-party apps even after the original credentials are revoked.
Inadequate Offboarding: Former employees might still access apps or data through unmanaged Google accounts.
Users can create personal Google accounts or sign up for the free Google Docs Essentials Starter plan using their company email.
This process needs no admin approval and can be done in minutes, providing users with a Google identity linked to the organization’s domain.
The G-Door vulnerability undermines several key security features of Microsoft 365:
Conditional Access policies become ineffective for these unmanaged accounts.
Device compliance and geolocation restrictions can be bypassed.
Data protection measures and legal compliance efforts are compromised.
Group-based access controls in Azure AD (Entra) can be circumvented.
To protect against the G-Door vulnerability, organizations should:
Implement strict domain verification processes for Google Workspace.
Regularly audit and manage unmanaged accounts associated with the company domain.
Enhance user education about the risks of creating personal accounts with work email addresses.
Consider implementing additional third-party security solutions to monitor and control access across multiple cloud platforms.
Organizations using cloud-based productivity suites must prioritize addressing vulnerabilities like G-Door to ensure strong security. IT administrators and security professionals need to stay alert and adjust their strategies to protect against new threats.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind