Google has announced Vanir, an open-source tool for detecting and fixing security vulnerabilities, publicly available for developers.
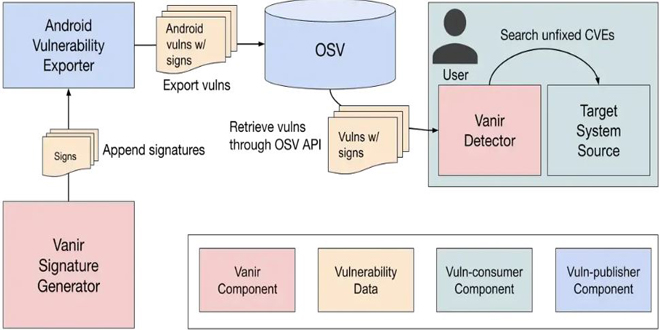
Vanir is a source code-based static analysis tool that automatically identifies the list of missing security patches in the target system. By default, Vanir pulls up-to-date CVEs from Open Source Vulnerabilities (OSV) together with their corresponding signatures so that users can transparently scan missing patches for an up-to-date list of CVEs.
By infosecbulletin
/ Sunday , September 21 2025
A new proof-of-concept tool named EDR-Freeze has been developed, capable of placing Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and antivirus solutions...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Sunday , September 21 2025
AI-driven malware called 'MalTerminal' utilizes OpenAI's GPT-4 to create harmful code like ransomware and reverse shells, indicating a major change...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Saturday , September 20 2025
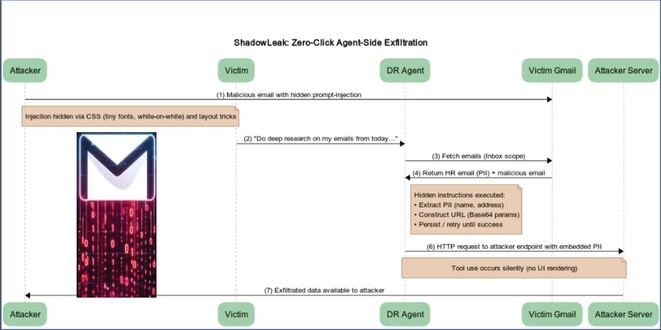
Cybersecurity researchers revealed a zero-click vulnerability in OpenAI ChatGPT's Deep Research agent that lets attackers leak sensitive Gmail inbox data...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Saturday , September 20 2025
Several European airports are experiencing flight delays and cancellations due to a cyber attack on a check-in and boarding systems...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Wednesday , September 17 2025
A threat actor claims to have breached Link3, a major IT solutions and internet service provider based in Bangladesh. The...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Wednesday , September 17 2025
Check point, a cyber security solutions provider hosts an event titled "securing the hyperconnected world in the AI era" at...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Tuesday , September 16 2025
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is one of the oldest and most persistent vulnerabilities in modern applications. Despite being recognized for over...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Monday , September 15 2025
Every day a lot of cyberattack happen around the world including ransomware, Malware attack, data breaches, website defacement and so...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Monday , September 15 2025
A critical permission misconfiguration in the IBM QRadar Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platform could allow local privileged users...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Monday , September 15 2025
Australian banks are now using bots to combat scammers. These bots mimic potential victims to gather real-time information and drain...
Read More
Vanir, originally designed for Android, provides an effective way to manage security patches for various devices and software versions. As Google’s blog states, “This strengthens the security of the Android ecosystem, helping to keep Android users around the world safe.”
What sets Vanir apart?
Source-Code-Based Static Analysis: Instead of using potentially inaccurate metadata, Vanir examines the source code directly, offering a more precise and thorough analysis.
Automated Patch Identification: Vanir automates the time-consuming task of finding missing patches, saving both time and resources.
Versatility: Although made for Android, Vanir can easily be used in other systems, making it a valuable asset across the software development landscape.
“A main focus of Vanir is to automate the time consuming and costly process of identifying missing security patches in the open source software ecosystem,” Google emphasizes in their blog.
Early Success and Future Potential:
Early use of Vanir has shown great results. Google states that one engineer generated signatures for over 150 vulnerabilities and verified missing security patches in just five days using Vanir.
Vanir’s open-source nature encourages teamwork and innovation in security. “By open-sourcing Vanir, we aim to empower the broader security community to contribute to and benefit from this tool, enabling wider adoption and ultimately improving security across various ecosystems,” says Google.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind