As of March 2024, X-Force is tracking the APT28 group is carrying out phishing campaigns using fake government and non-governmental organization documents to target different regions around the world, including Central Asia, Europe, the South Caucasus, and North and South America.
The discovered lures include a mix of public and internal documents. They are related to various fields such as critical infrastructure, finance, cybersecurity, executive engagements, healthcare, maritime security, defense industrial production, and business. The cybersecurity firm is monitoring the activity cluster known as ITG05 or Fancy Bear, BlueDelta, Blue Athena, Fighting Ursa, UAC-028, TA422, Sofacy, Sednit, Pawn Storm, Iron Twilight, and FROZENLAKE.
After three months of revealing that the threat actor used lures related to the Israel-Palestine war to spread a custom backdoor called HeadLace, a follow-up is necessary. APT28 has targeted Ukrainian government entities and Polish organizations with phishing emails containing implants and infostealers like OCEANMAP, MASEPIE, and STEELHOOK.
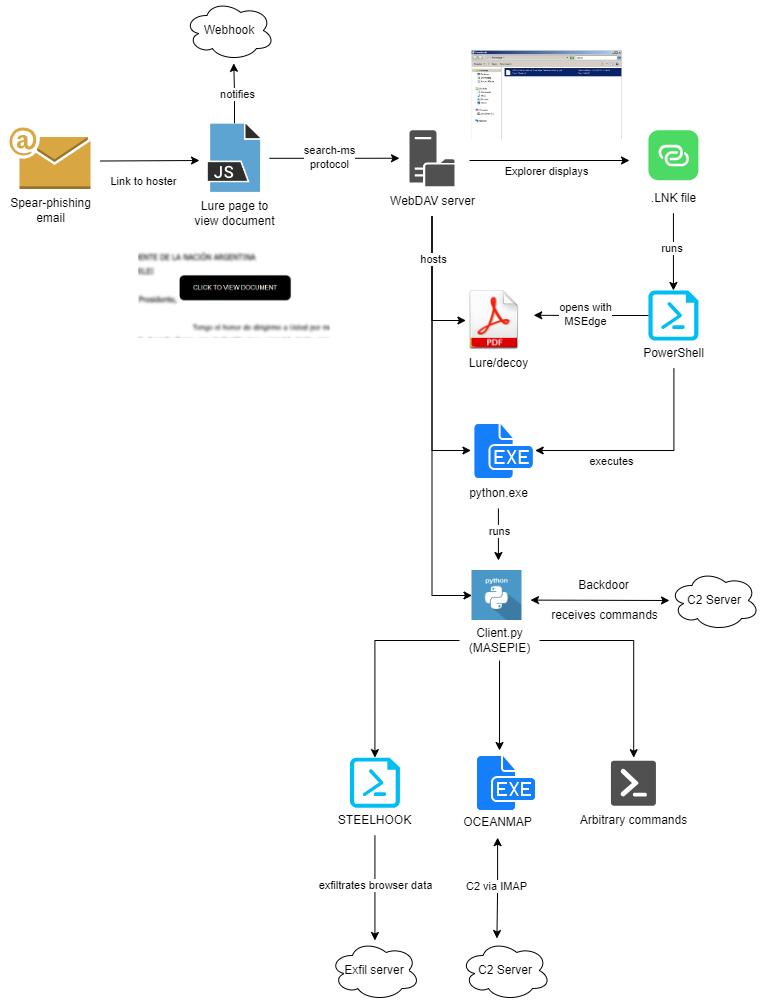
“Beginning in November 2023, we observed ITG05 using the “search-ms” URI handler, a new technique for the group, leading victims to download malware hosted on actor-controlled WebDAV servers,” said the cybersecurity analysts.
Other attacks by the opponent used weaknesses in Microsoft Outlook (CVE-2023-23397, with a score of 9.8) to steal NTLMv2 hashes. This could allow the threat actor to exploit other weaknesses to take and use these hashes in relay attacks.
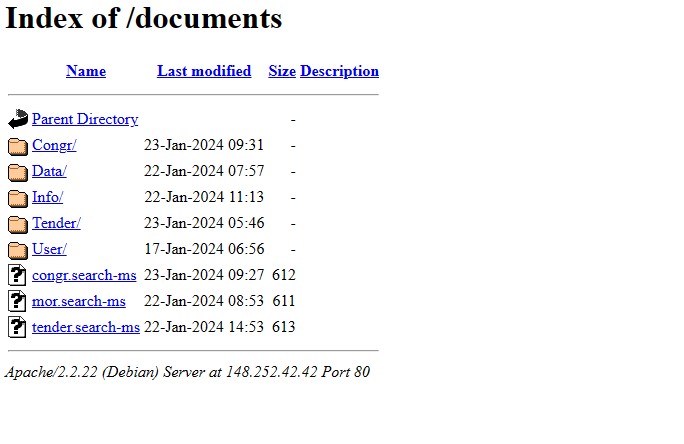
Between late November 2023 and February 2024, there were campaigns that used Microsoft Windows’ “search-ms:” URI protocol handler to trick users into downloading malware from WebDAV servers. These servers and the MASEPIE C2 servers may be hosted on compromised Ubiquiti routers, which was a botnet taken down by the U.S. government.
Phishing attacks pretend to be from different countries such as the U.S., Azerbaijan, Armenia, Poland, Kazakhstan, Belarus, Georgia, Ukraine, and Argentina. They use government and non-government documents to start the infection process. The attacks end with the use of malware like MASEPIE, STEELHOOK, and OCEANMAP. These malware can steal files and browser data, as well as execute commands.
APT28 is capable of adapting to new opportunities by utilizing new methods of infection and taking advantage of easily accessible infrastructure. They also constantly update their malware arsenal.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind