A new study found that a highly accurate artificial intelligence system, similar to ChatGPT, was trained with the life stories of over a million people. This system can predict individuals’ lives and their risk of early death.
Scientists from the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) have trained an AI model on the personal data of Denmark’s population. This model was found to accurately predict the likelihood of people dying better than any other existing system.
Researchers studied health and labor market data from 6 million people in Denmark. The data was collected from 2008 to 2020 and included information about education, doctor visits, hospital visits, diagnoses, income, and occupation.
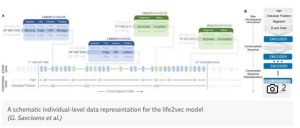
Scientists transformed the dataset into words to train a big language model called “life2vec,” similar to the technology used in AI apps like ChatGPT.
According to a study published in the journal Nature Computational Science on Tuesday, once the AI model understood the patterns in the data, it could accurately predict outcomes like personality and time of death better than other advanced systems.
Researchers collected data on a group of people aged 35 to 65. Half of the group passed away between 2016 and 2020. They then used an AI system to predict which individuals survived and which ones did not.
Its predictions were found to be 11% more accurate than any other existing AI model or the method used by life insurance companies to price policies.
“What’s exciting is to consider human life as a long sequence of events, similar to how a sentence in a language consists of a series of words,” study first author Sune Lehman from DTU said.
This is usually the type of task for which transformer models in AI are used, but in our experiments, we use them to analyze what we call life sequences, i.e., events that have happened in human life,” Dr Lehman said.
Researchers used a model to find out the likelihood of a person dying within four years.
The study discovered that the model’s responses support previous findings. When considering all other factors, it shows that people in positions of leadership or with a high income are more likely to survive. On the other hand, being male, skilled, or having a mental diagnosis is linked to a higher risk of death.
“We used the model to address the fundamental question: to what extent can we predict events in your future based on conditions and events in your past?” Dr Lehman said
“Scientifically, what is exciting for us is not so much the prediction itself, but the aspects of data that enable the model to provide such precise answers,” he added.
The model can predict personality test outcomes better than current AI systems for a specific part of the population.
“Our framework allows researchers to identify new potential mechanisms that impact life outcomes and associated possibilities for personalized interventions,” researchers wrote in the study.
Scientists advise against life insurance companies using the model due to ethical concerns.
“Clearly, our model should not be used by an insurance company, because the whole idea of insurance is that, by sharing the lack of knowledge of who is going to be the unlucky person struck by some incident, or death, or losing your backpack, we can kind of share this burden,” Dr Lehman told New Scientist.
Researchers warn about ethical issues related to the use of life2vec, including the protection of sensitive data, privacy concerns, and the influence of bias in data.
“We stress that our work is an exploration of what is possible but should only be used in real-world applications under regulations that protect the rights of individuals,” they said.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind