BGD e-GOV CIRT report highlights a recent surge in phishing attacks targeting Bangladeshi government organizations, law enforcement, and educational institutions. These attacks aim to steal sensitive information by impersonating official entities and using malicious attachments and links.
Key details include:
Target Sectors:
Government organizations
Law enforcement agencies
Educational institutions
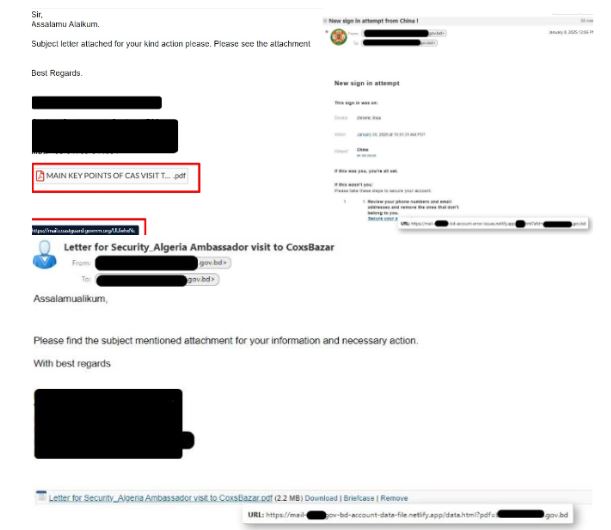
Phishing Characteristics:
Subject and Sender: Mimic official communications, often appearing as security updates.
Body Content: Urges urgent action (e.g., clicking links or downloading attachments), using formal language and references to official documents.
Attachments: Malicious files (e.g., .rar, .pdf, .html) and renamed files to bypass filters.
Phishing Links: Redirect to fake login pages or forms that collect sensitive data.
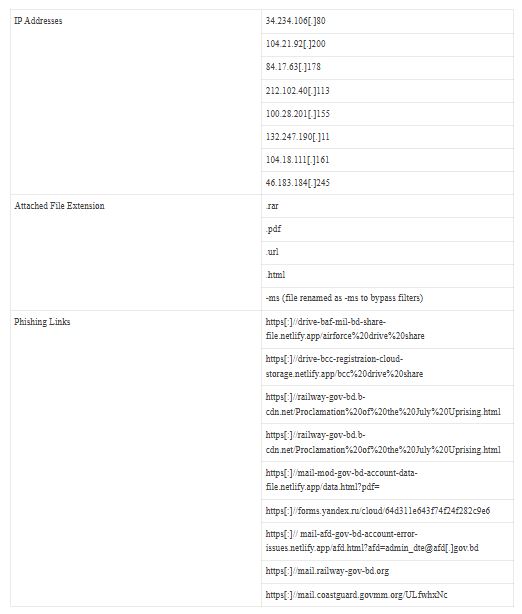
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs):
Domain Spoofing: This domain is made to look like real government websites but is hosted on netlify.app, a free hosting service.
Non-functional Links: Placeholder links (https[:]// briefcase, https[:]// remove) highlight a lack of legitimacy.
Attachment Mismatch: The email references an attachment, but the link leads to a questionable page instead of the file.
Content Encoding: The email content is encoded, making it harder to read easily.
Detection Rules:
Suricata Rules to detect phishing URLs and IPs.
Sigma Rules to identify suspicious IP connections and phishing links in network logs.
Mitigation Actions:
Be Alert: Avoid clicking unknown links and downloading suspicious attachments.
Report Phishing: Forward suspicious emails to IT/security teams.
Protect Credentials: Never share login details through email; enable multi-factor authentication.
Training: Stay informed on phishing tactics and red flags.
Monitoring: Use IOCs, Suricata, and Sigma rules for threat detection and continuous system monitoring.
System Security: Patch systems, apply the principle of least privilege, and use email filtering.
Incident Response: Ensure a tested plan and report incidents to BGD e-GOV CIRT.
These recommendations are aimed at reducing the risk of successful phishing attacks through vigilance, timely detection, and system security measures.
Alert! Fake Crowdstrike Recruitment Emails Spread XMRig cryptominer
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind