Microsoft Threat Intelligence released findings from their investigation on the Russian threat group known as Forest Blizzard (STRONTIUM). The group used a specialized tool to gain higher privileges and steal login information in compromised networks.
Since June 2020, and maybe even since April 2019, Forest Blizzard has been using a tool called GooseEgg to take advantage of the CVE-2022-38028 vulnerability in the Windows Print Spooler service. They do this by modifying a JavaScript constraints file and running it with SYSTEM-level permissions.
Microsoft has observed the hacking group Forest Blizzard using a program called GooseEgg to attack government, non-governmental, education, and transportation sector organizations in Ukraine, Western Europe, and North America. GooseEgg is a simple application, but it can be used to launch other applications with special permissions. This allows hackers to do things like execute code remotely, install a backdoor, and move around within compromised computer networks.
Forest Blizzard often uses publicly available exploits in addition to CVE-2022-38028, such as CVE-2023-23397. Linked to the Russian General Staff Main Intelligence Directorate (GRU) by the United States and United Kingdom governments, Forest Blizzard primarily focuses on strategic intelligence targets and differs from other GRU-affiliated and sponsored groups, which Microsoft has tied to destructive attacks, such as Seashell Blizzard (IRIDIUM) and Cadet Blizzard (DEV-0586).
Although Russian threat actors are known to have exploited a set of similar vulnerabilities known as PrintNightmare (CVE-2021-34527 and CVE-2021-1675), the use of GooseEgg in Forest Blizzard operations is a unique discovery that had not been previously reported by security providers.
Microsoft is committed to providing visibility into observed malicious activity and sharing insights on threat actors to help organizations protect themselves. Organizations and users are to apply the CVE-2022-38028 security update to mitigate this threat, while Microsoft Defender Antivirus detects the specific Forest Blizzard capability as HackTool:Win64/GooseEgg.
Launch, persistence, and privilege escalation:
Microsoft has observed that, after obtaining access to a target device, Forest Blizzard uses GooseEgg to elevate privileges within the environment. GooseEgg is typically deployed with a batch script, which we have observed using the name execute.bat and doit.bat. This batch script writes the file servtask.bat, which contains commands for saving off/compressing registry hives. The batch script invokes the paired GooseEgg executable and sets up persistence as a scheduled task designed to run servtask.bat.
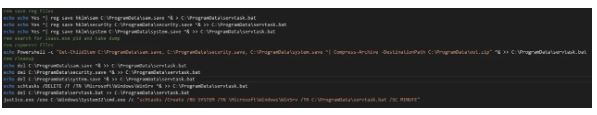
Figure 1. Batch file
The GooseEgg binary—which has included but is not limited to the file names justice.exe and DefragmentSrv.exe—takes one of four commands, each with different run paths. While the binary appears to launch a trivial given command, in fact the binary does this in a unique and sophisticated manner, likely to help conceal the activity.
The first command issues a custom return code 0x6009F49F and exits; which could be indicative of a version number. The next two commands trigger the exploit and launch either a provided dynamic-link library (DLL) or executable with elevated permissions. The fourth and final command tests the exploit and checks that it has succeeded using the whoami command.
Microsoft has observed that the name of an embedded malicious DLL file typically includes the phrase “wayzgoose”; for example, wayzgoose23.dll. This DLL, as well as other components of the malware, are deployed to one of the following installation subdirectories, which is created under C:\ProgramData. A subdirectory name is selected from the list below:
Microsoft
Adobe
Comms
Intel
Kaspersky Lab
Bitdefender
ESET
NVIDIA
UbiSoft
Steam
Click here to read the full story.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind














