Three emerging threats will be discussed below, along with how sandbox analysis can be utilized to detect them proactively.
Lockbit Ransomware:
The Lockbit ransomware is a major cybersecurity threat that appeared in 2019. It works as Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), where affiliates use its software to carry out attacks. The Royal Mail was one of its main targets, and the attackers demanded an exceptionally high ransom of $80 million.
Lockbit ransomware uses the AES encryption algorithm to encrypt files, and then it encrypts the AES key using the RSA algorithm. This double encryption makes it very difficult for victims to recover their data without the decryption key.
The Lockbit ransomware has consistently evolved, with the most recent version being Lockbit v3, also known as Lockbit Black.
Despite a coalition of law enforcement agencies dismantling its infrastructure in early 2024, Lockbit has now resumed its operations.
Detecting and Analyzing LockBit Black Ransomware in a Sandbox:
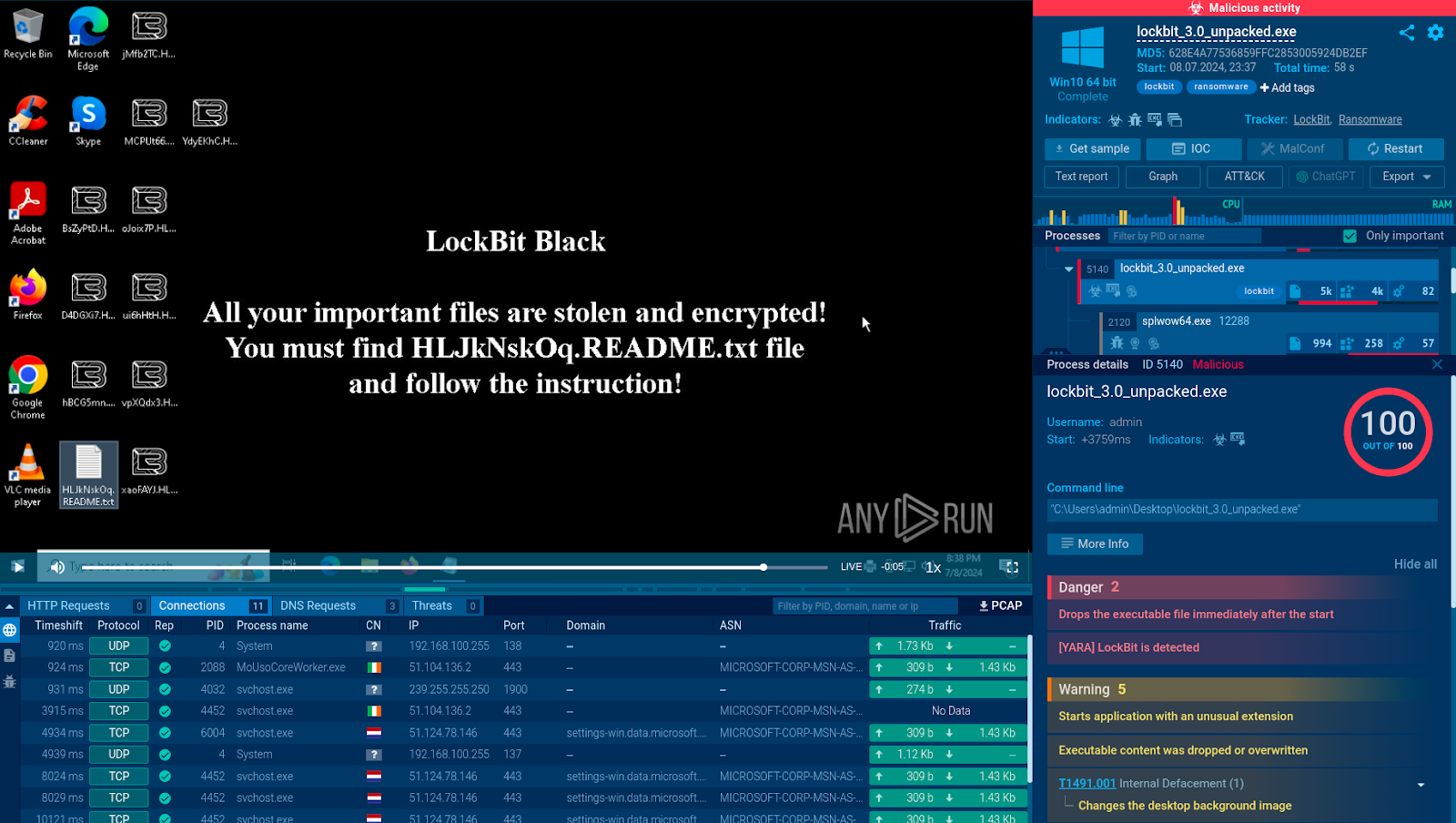
To avoid a LockBit infection, we can proactively analyze all suspicious files, including email attachments, in a sandbox.
As part of the analysis, we can observe:
- CMSTMLUA process that performs privilege escalation, allowing the ransomware to gain higher-level access to the system.
The desktop wallpaper change is a common tactic ransomware operators use to notify victims of compromised systems.
A ransom note file containing instructions and Tor URLs for communicating with the attackers.
The sandbox provides a conclusive verdict, classifying the analyzed file as exhibiting malicious activity.
Bluesky Ransomware:
The BlueSky ransomware, detected in Q2 of 2022, is still a major cybersecurity threat. It targets the Windows multithreading architecture to encrypt files faster. This harmful software uses advanced encryption techniques with the ChaCha20 algorithm. It can also spread to other devices on the same network.
After encrypting the files, the ransomware changes their names by adding the .bluesky extension. It also creates a ransom instruction file, instructing victims to pay a ransom by accessing a page on Tor.
Detecting and Analyzing BlueSky Ransomware in a Sandbox:
Despite BlueSky’s anti-analysis functionality, we can easily expose it by uploading its sample to a free malware sandbox like ANY.RUN, which offers a safe virtual environment for detonating it.
See this analysis session for more details.
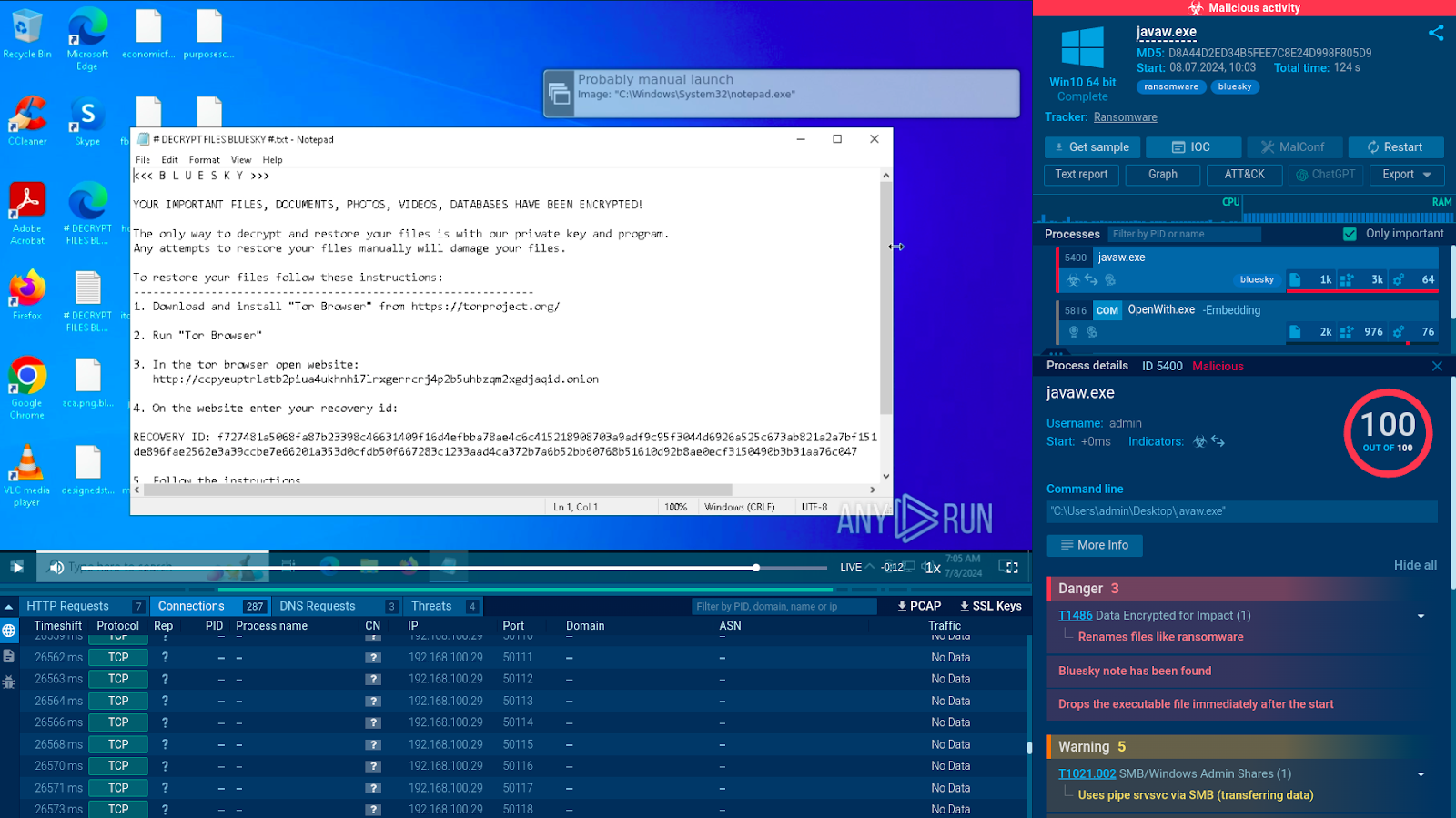
Analysis of the Bluesky ransomware in the ANY.RUN sandbox:
The service instantly detects the malware and notifies us about its presence by adding the corresponding tags “bluesky” and “ransomware”. It also lists the activities carried out by the program including:
File renaming.
Creation and dropping of a ransom note containing instructions on how to decrypt the locked files. Thanks to its interactivity, the sandbox lets us open this note manually and read its contents.
Analysis also reveals that the note contains a TOR network URL, which the victim is instructed to visit to make the ransom payment.
After analysis is complete, we receive a detailed report with all the important information gathered during the file execution, including indicators of compromise.
Beast Ransomware:
Beast ransomware, also known as Monster ransomware, emerged in March 2022. It is built on the Delphi programming language and has the ability to attack both Windows and Linux systems.
The malware doesn’t affect users in CIS countries, indicating that the creators might be from that region. The Beast ransomware uses a high-level encryption method and also archives the encrypted files.
The malware is mainly spread through email attachments and links, taking advantage of people’s vulnerability to phishing attacks. Despite being a new type of ransomware, Beast has the potential to become a serious and widespread threat, similar to LockBit.
Detecting and Analyzing Beast Ransomware in a Sandbox:
By running suspicious files and URLs in a sandbox, we can easily expose Beast and other malware.
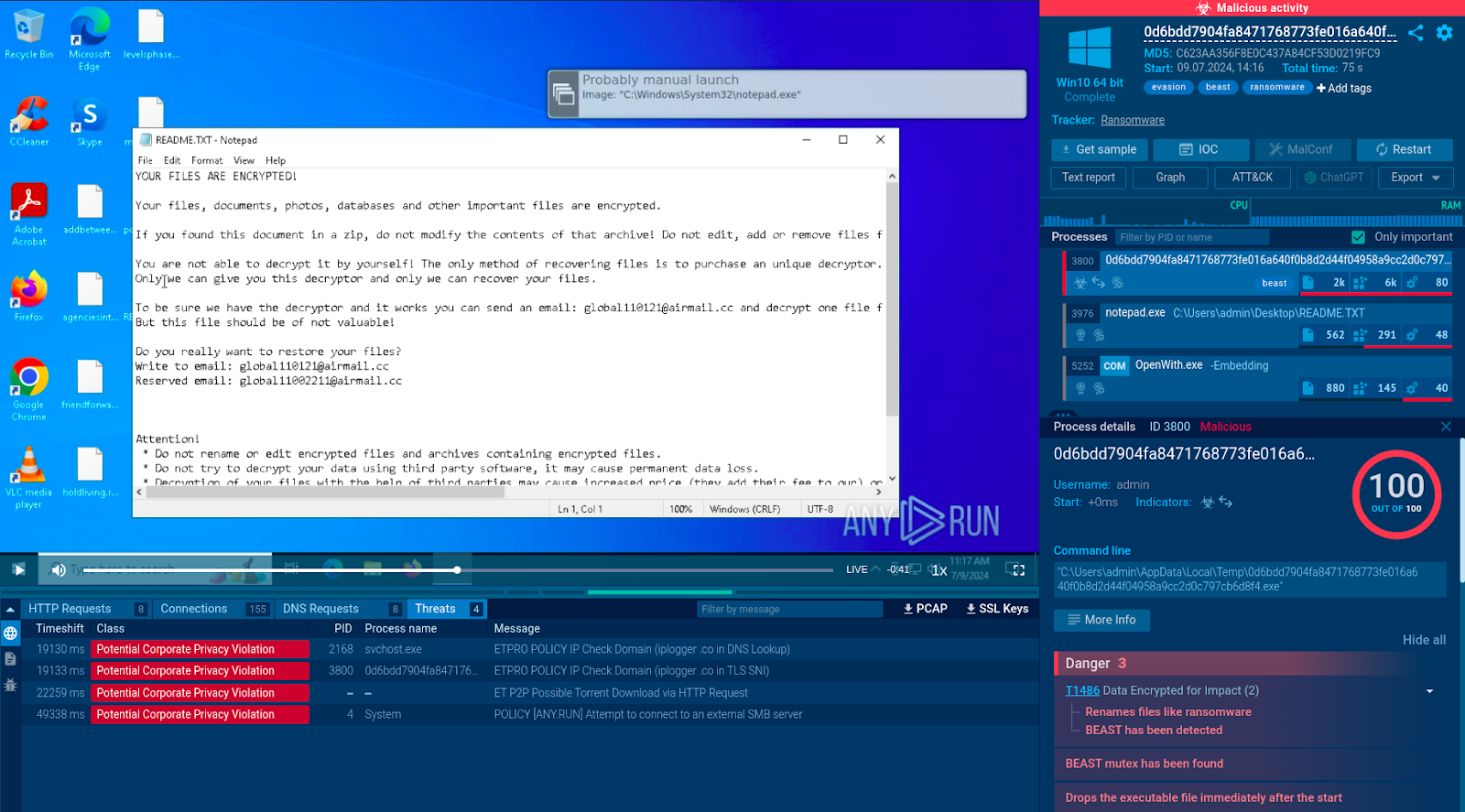
Consider this analysis session.
Some of the Beast activities detected by the service include:
Installation of a mutex characteristic of the Beast malware.
Attempt to obtain the host’s IP address.
Connection to an external SMB server.
Analyze Suspicious Files and URLs in ANY.RUN
ANY.RUN sandbox allows you to interactively analyze malware. You can safely engage with files and links in a virtual environment to investigate the full extent of each threat.
The service finds and lists all activities in network traffic, registry, file system, and processes, and extracts signs of compromise.
Source: cybersecuritynews.com
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind