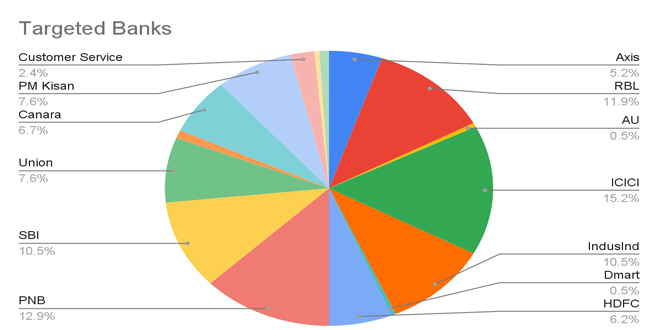
The zLabs research team found a mobile malware campaign with nearly 900 malware samples aimed at Indian bank users. Analysis shows shared code, interfaces, and logos, indicating a single group behind the attacks on Android devices. Zimperium’s detection engine successfully identified these as Trojan Bankers targeting Indian financial institutions.
This malware campaign differs from typical banking Trojans that steal one-time passwords (OTPs) via command-and-control servers. Instead, it uses live phone numbers to redirect SMS messages, creating a traceable digital trail for law enforcement. Our team has identified about 1,000 phone numbers associated with this campaign.
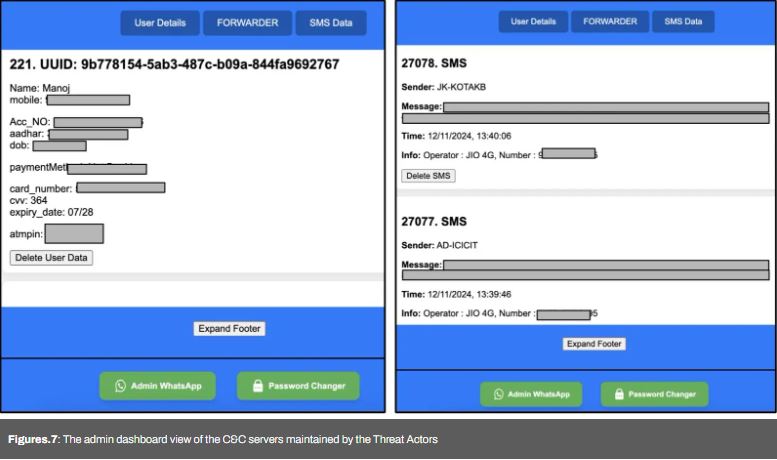
Researchers found over 222 publicly accessible Firebase storage buckets containing 2.5GB of sensitive data, including SMS messages from Indian banks, bank details, card information, and government IDs. This exposure affects around 50,000 users, highlighting the serious scope of the issue.
How the Malware Works:
The malware is distributed via WhatsApp as fake app files that look like real government or banking apps. Once installed, these apps trick users into sharing sensitive information by imitating real banking apps. The malware uses SMS permissions to steal messages, including one-time passwords (OTPs), allowing for unauthorized transactions.
Variants and Data Exposure:
The FatBoyPanel malware family includes three distinct variants:
SMS Forwarding: Captures SMS messages and forwards them to attacker-controlled phone numbers.
Firebase Exfiltration: Sends stolen SMS data to Firebase endpoints acting as command-and-control (C&C) servers.
Hybrid: Combines both methods for data exfiltration.
Researchers identified over 1,000 malicious applications linked to this campaign.
These apps use code obfuscation to avoid detection and complicate reverse engineering. Data leaked through Firebase endpoints was publicly accessible because of inadequate authentication. Sensitive information of about 50,000 users was exposed, including bank account details and government IDs.

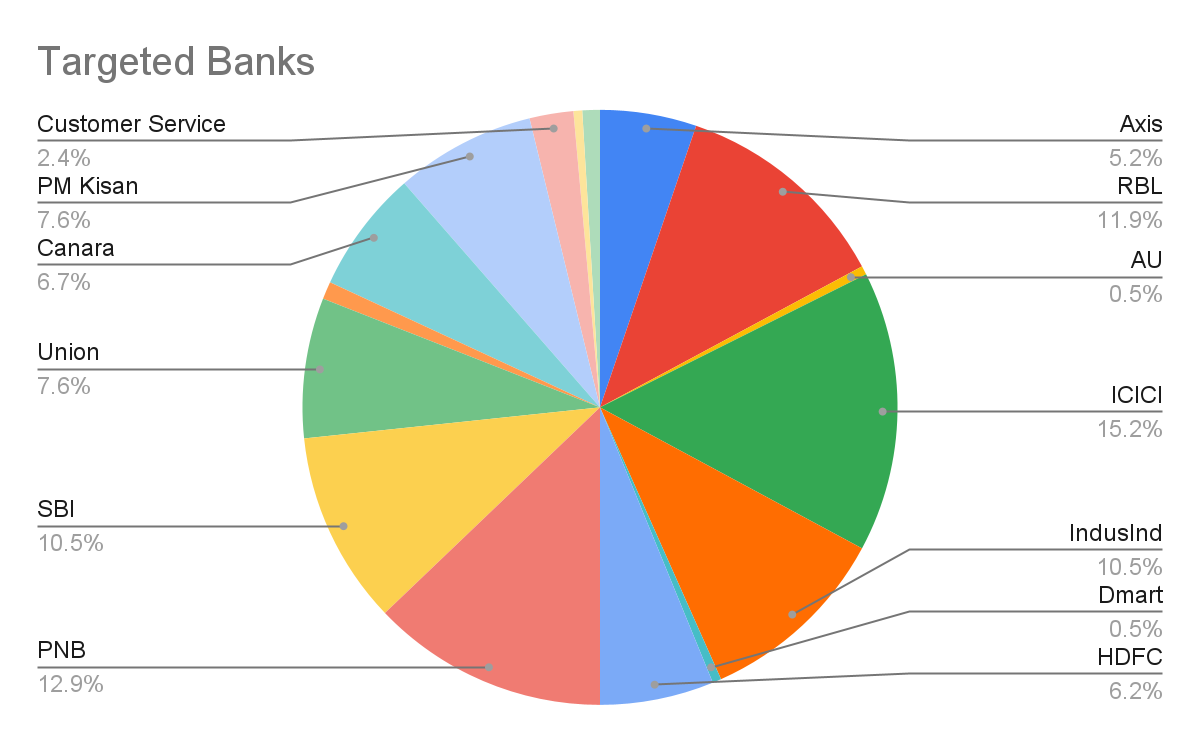
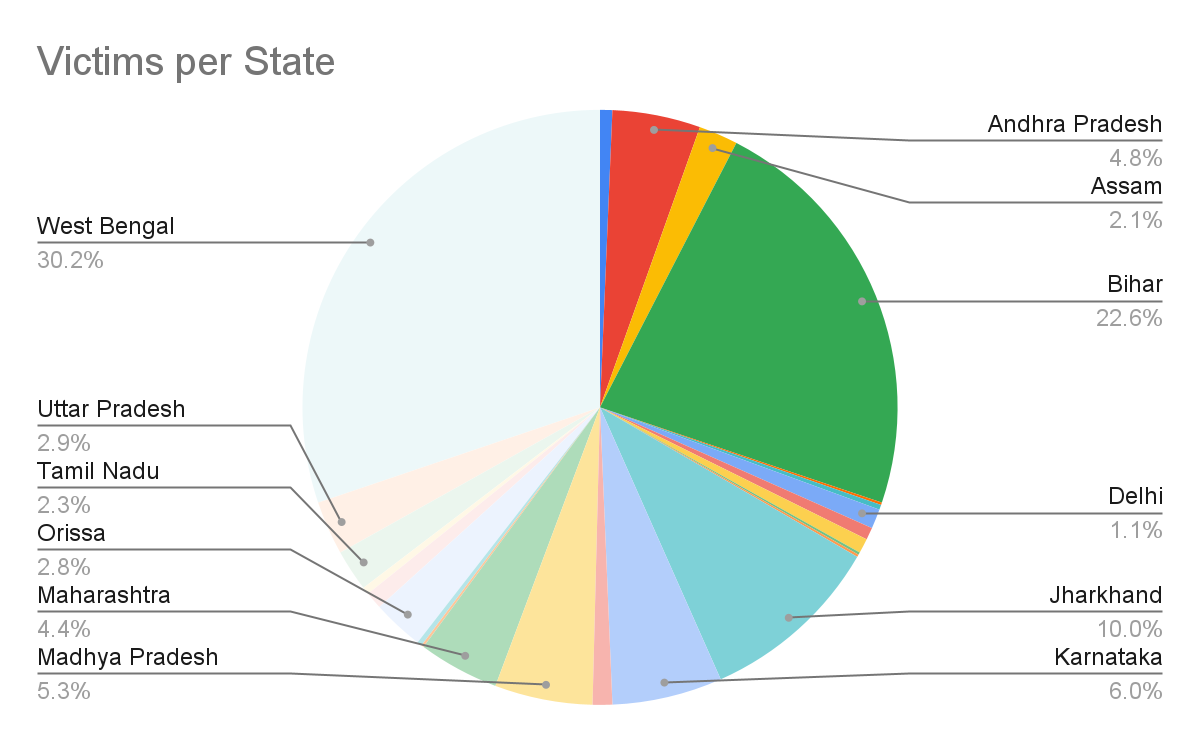
Zimperium found that most attackers’ phone numbers were registered in West Bengal, Bihar, and Jharkhand. The campaign imitated major Indian banks by copying their app icons and interfaces to boost credibility.
India’s growing dependence on digital payments highlights the need for strong cybersecurity. Individuals and institutions must stay alert against threats like the FatBoyPanel campaign to protect financial data.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind