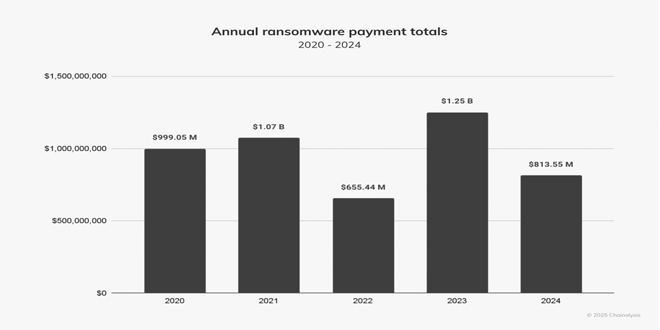
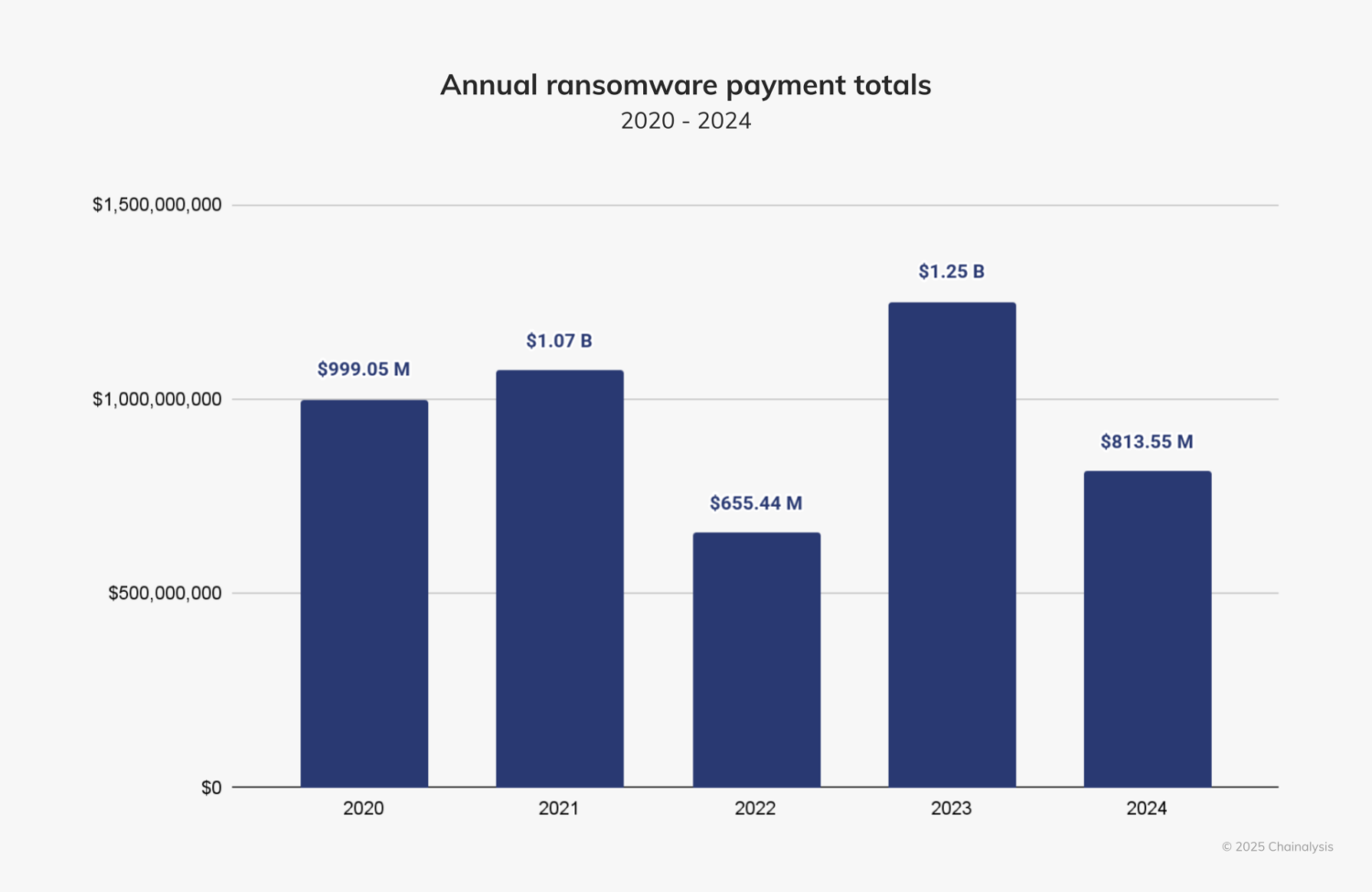
Ransomware payments dropped by 35% last year compared to 2023, despite an increase in the number of attacks, according to a new report from Chainalysis.
Despite claims from cybersecurity firms that ransomware activity peaked in 2024, there has been a significant drop in extortion payments. Chainalysis also noted in its mid-year report that ransomware attacks were expected to increase, but they slowed down in the second half of the year.
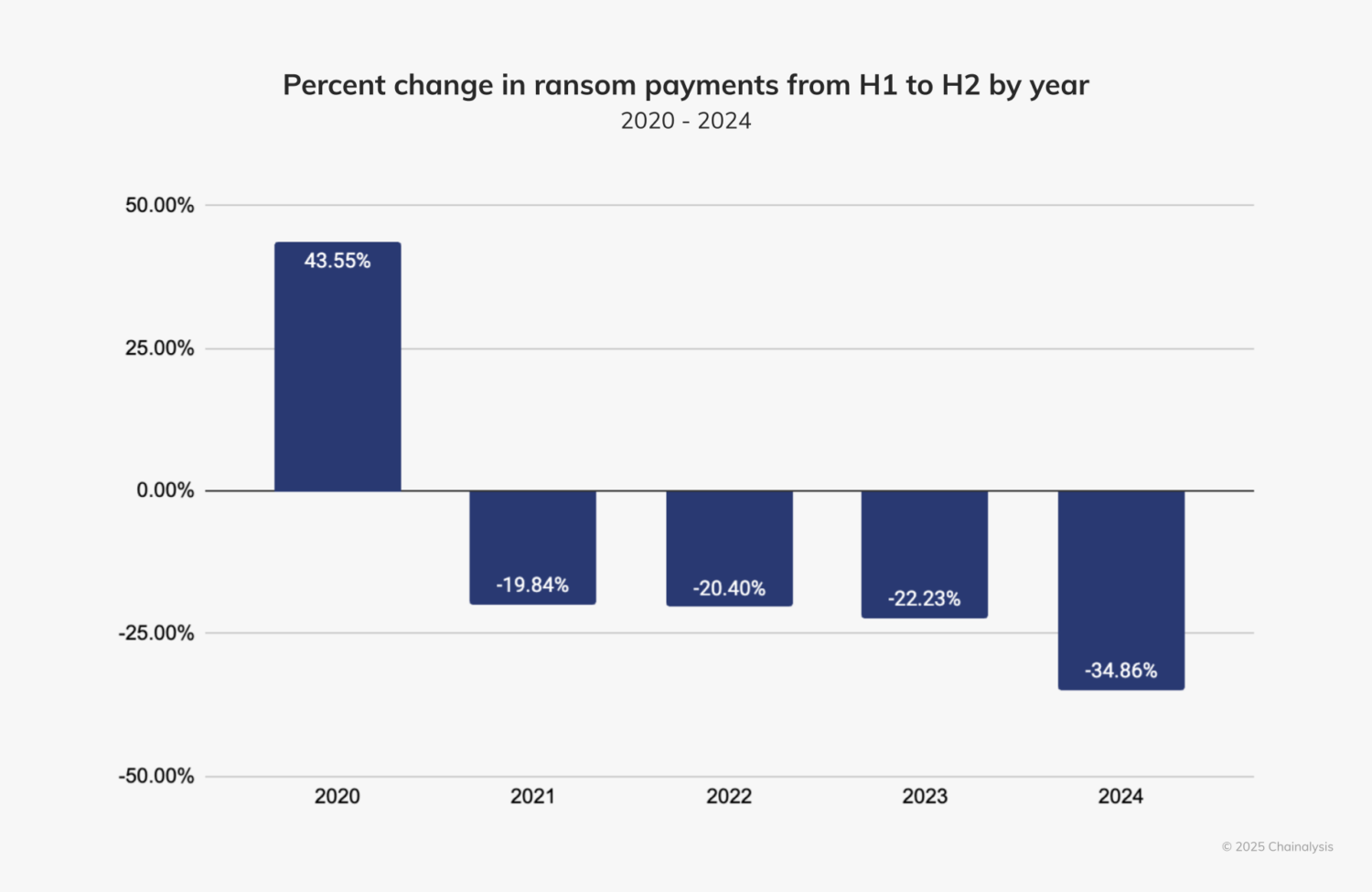
Chainalysis tracked $812.55 million in payments in 2024, a decrease from $1.25 billion in 2023..
“Despite its small half-over-half (HoH) increase, we expected 2024 to surpass 2023’s totals by the end of the year,” the company wrote on its website. “Fortunately, however, payment activity slowed after July 2024 by approximately 34.9%. This slowdown is similar to the HoH decline in ransom payments since 2021 and the overall decline during H2 2024 in some types of crypto-related crime, such as stolen funds. Notably, the decline this year is more pronounced than in the last three years.”
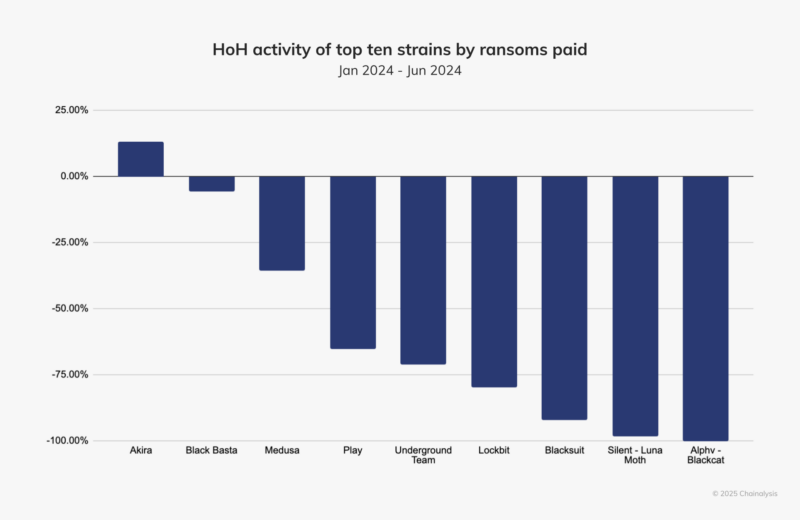
Disruptions of major ransomware groups like LockBit and ALPHV/BlackCat have led to a decrease in ransomware payments. Agencies like the UK’s National Crime Agency and the FBI significantly reduced LockBit’s activity, while ALPHV/BlackCat abandoned its affiliates after attacking Change Healthcare.
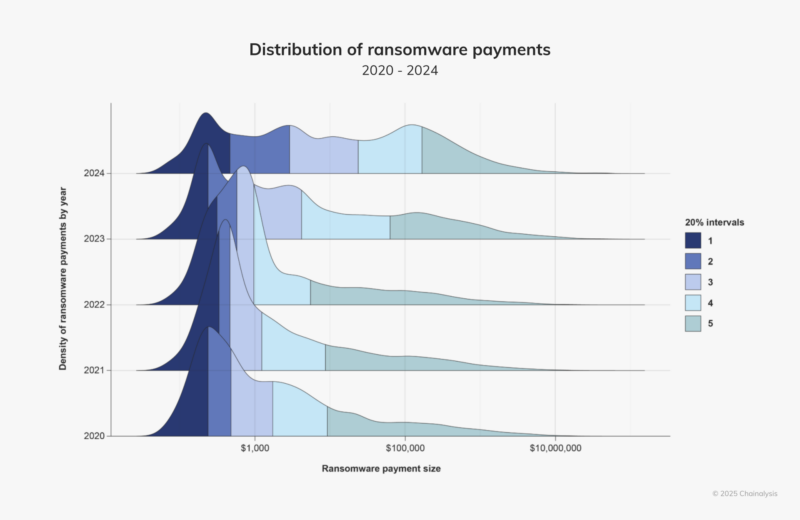
Ransomware groups typically emerge after law enforcement breaks up leading ones. However, after LockBit and BlackCat disappeared, no major group filled the gap. Instead, smaller groups targeted small to medium-sized victims and demanded lower ransoms, according to a Chainalysis report.
The company reports that more organizations are resisting attacks by opting not to pay ransoms and instead using improved cybersecurity practices and backups for recovery.
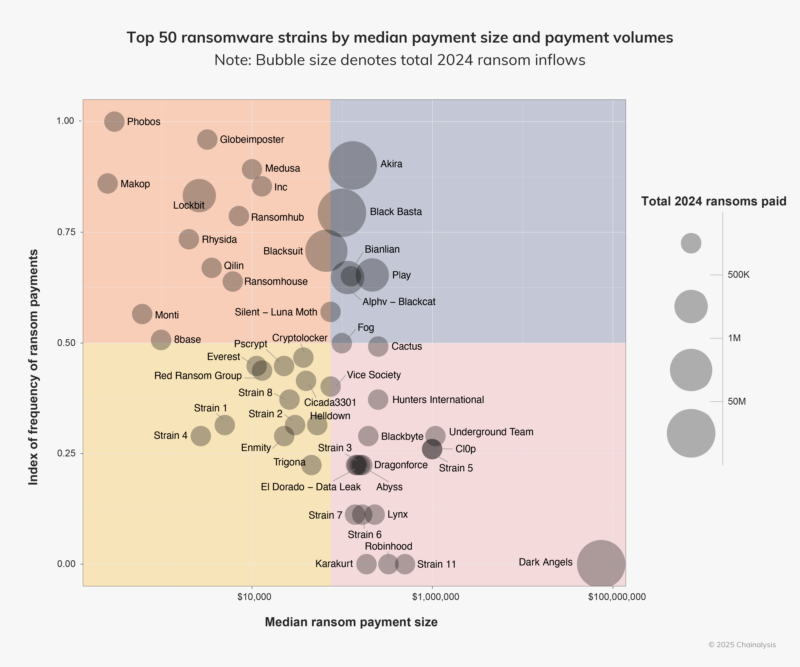
Despite reduced payments, ransomware groups like Akira and INC are gaining attention for using rebranded, leaked, or purchased code. They are also skilled at exploiting vulnerabilities, especially in enterprise settings, showing increased speed and aggression in their tactics.
Chainalysis reports that law enforcement actions have changed how ransomware operators handle financial transactions. They are now less dependent on mixers to hide fund movements and are using cross-chain bridges and centralized exchanges instead.
The company reports that actors are leaving ransomware in wallets and avoiding money transfers, partly due to fear of being monitored by law enforcement.
“It’s worth calling out the substantial volumes of funds being held in personal wallets,” the report reads. “Curiously, ransomware operators, a primarily financially motivated group, are abstaining from cashing out more than ever.”
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind