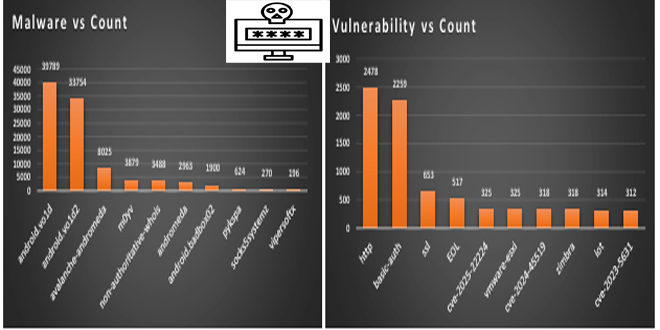
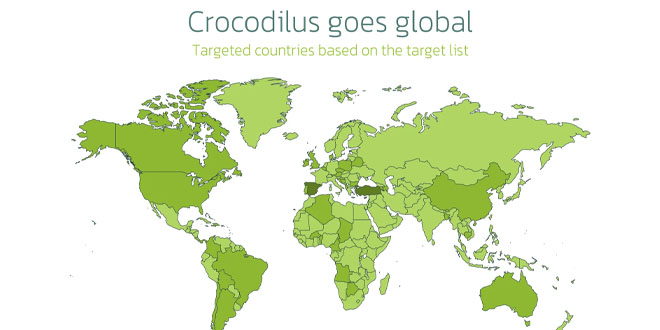
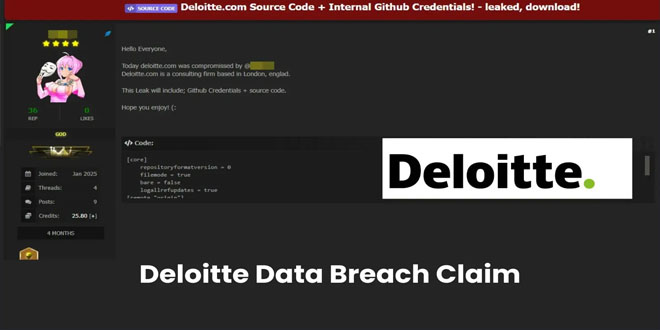
Expert instructors from the SANS Institute here yesterday detailed what they cite as the most dangerous forms of cyberattacks for 2023.
Some of the key themes bubbling to the surface included the intersection of AI with attack patterns and the ways that attackers are taking advantage of highly flexible development environments.
“This is my favorite panel of the year,” said Ed Skoudis, president of SANS Technology Institute College and moderator of the panel, who introduced SANS panelists as both teachers for his organizations as well as expert practitioners with real-world experience about what’s currently going down in the attack landscape.
“These are the folks that I turn to and a whole lot of other folks turn to get the latest on what the attacks are all about and what we need to do to defend against them,” he said.
1. SEO-Boosted Attacks
Just as regular businesses utilize search engine optimization (SEO) to boost the rankings of certain terms for the sake of marketing their products and driving traffic to revenue-generating sites, the bad guys also turn to SEO. In their case they use it to boost the rankings of their malware-laden sites in order to send more victims their way, explained Katie Nickels, senior director of digital intelligence for Red Canary and a SANS instructor. She said that as security defenders do a better job of blocking outbound clicks to malicious sites by blocking phishing attempts and the like, the attackers are adjusting by luring them through watering hole attacks. And SEO is playing into that scheme.
“So, imagine some of you are in marketing and you’re using search engine optimization to get your company’s results to the top,” explained Nickels. “Well, adversaries do the same thing, but for evil, right? They use keywords and other SEO techniques to make sure their results, their malicious websites, are at the top of those search engine results.”
Nickels walked through an example of a GootLoader attack that was propagated by using SEO to boost the rankings of a search for “legal agreements” to target unsuspecting users searching for an easy download of a legal document template.
2. Malvertising
Similar to how marketers utilize both organic search techniques via SEO and paid search techniques utilizing advertising, cybercriminals are doing the same. Nickels said drive-by attacks are also similarly fueled by malicious advertising (malvertising) campaigns that artificially boost the rankings of sites for certain keywords.
“And fun fact, I did not actually plan this but malvertising was just added to MITRE ATT&CK as a new technique yesterday,” she said.
The example she brought to light in this case was a lookalike campaign for a free piece of 3D graphic software called Blender.
“Search for that and you get a couple ads and a couple of results,” she said. “That first ad, that’s bad. Second one, if I click that, that would also be into a malicious website. The third one’s gotta be legit, right? No, in this case, the third ad was also malicious. It’s not until the fourth result on that keyword that you get the legitimate software website.”
Adding to the challenge of these high rankings, she explained that the lookalike sites are near identical to the actual Blender website, as the bad guys are getting really good at mimicking certain sites like this.
While neither SEO-boosted attacks nor malvertising are brand-new techniques, she noted, the reason she put them at the top of her list is the increasing prevalence of these attacks this year.
3. Developers as a Target
Johannes Ullrich, dean of research for SANS Technology Institute College and head of the Internet Storm Center, said his pick for the year is cyberattacks targeting software and application developers.
“What I noticed last year, I think that’s something that’s really going to increase, is that attacks are specifically targeting developers,” Ullrich said. “We talk a lot about dependencies and malicious components. The first individual in your organization that’s exposed to these malicious components is the developer.”
Developers are an extremely enticing target as they usually have elevated privileges across IT and business systems, the systems they use can be subverted to poison the software supply chain, and they tend to work on machines that are less locked down than the average user in order to enable them to experiment with code and ship software on the daily.
“A lot of this endpoint protection software is sort of geared towards your random corporate workstation,” Ullrich said. “They’re not necessarily used to or designed to protect systems that have developer tools installed.”
4. Offensive Uses of AI
With the explosion of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, defenders should expect attackers — even very non-technical ones — to ramp up their development of exploits and zero-day discovery utilizing these AI tools. This was the attack technique highlighted by Steven Sims, offensive operations curriculum lead for SANS and a longtime vulnerability researcher and exploit developer.
Sims walked through the ease with which he could get ChatGPT to uncover a zero-day. He demonstrated some prompts he used by pointing it at a piece of code vulnerable to the SigRed DNS flaw that recently came to light and had it explore that code to find the flaw as if it was a zero-day flaw.
Additionally, he demonstrated the prompts he used to get ChatGPT to help him write code for a simple piece of ransomware. Though ChatGPT does have some protections built into the system to refuse to develop ransomware code, he was able to convince it by breaking the pieces down into discrete parts.
“From a defensive perspective, there is basically nothing you can do. Sorry,” Sims told the audience. “Defensive depth is important. Expert mitigations is important. Understanding how this works is important. Writing your own AI and machine learning to understand more about it is important. These things are really all you can do because it’s out there and it’s amazing.”
5. Weaponizing AI for Social Engineering
In addition to technical offensive uses of AI, expect attackers this year to drastically ramp up their use of AI to make their social engineering and impersonation attempts highly believable, warned Heather Mahalik, director of digital intelligence for Cellebrite and digital forensics and incident response lead for SANS.
She illustrated her point with a social engineering experiment she did with her son, prompting ChatGPT to write convincing texts — with emojis — that would make them sound like a 9-year-old girl trying to get her son to tell her his address.
“It can be used to target people in your organizations,” she said. “I chose to target my son because I tried to make everything really personable and show that we’re all attackable.”
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind