Researchers have demonstrated a method to bypass Windows 11’s BitLocker encryption, enabling the extraction of Full Volume Encryption Keys (FVEKs) from memory.
This vulnerability underscores the risks associated with physical access attacks and highlights potential weaknesses in memory protection mechanisms.
The attack revolves around capturing the contents of a computer’s RAM during operation.
If an attacker has physical access to a device, they can abruptly restart it and dump the memory to extract sensitive information, including FVEKs.
This process leverages the fact that encryption keys are temporarily stored in memory while the system is running.
However, the technique is not foolproof. RAM contents degrade rapidly when power is cut off, making it crucial to minimize downtime.
To mitigate this degradation, researchers said that attackers could use methods such as physically cooling the RAM or maintaining power delivery using external sources.
In one demonstration, the attacker shorted the reset pins on the motherboard to restart the system without cutting power, preserving memory integrity.
Secure Boot, a security standard designed to prevent unauthorized software from running during startup, presents another layer of protection.
However, it has known vulnerabilities and can be bypassed using techniques such as shims or other exploits. These methods allow attackers to load custom tools for memory analysis.
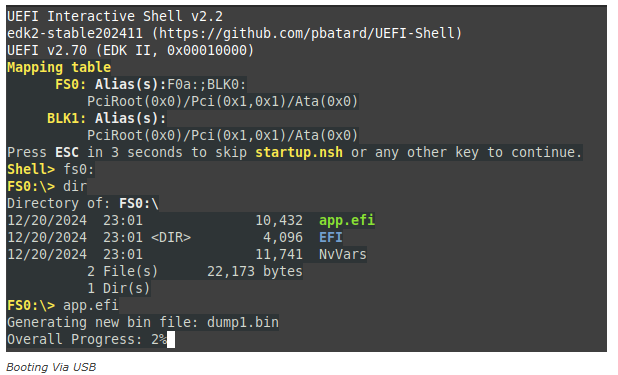
1. Create a Bootable USB Device: A USB drive larger than the target system’s RAM is prepared with specialized software to extract memory dumps.
2. Abruptly Restart the Target System: The system is restarted at a critical moment—such as during Windows loading but before reaching the login screen—to capture encryption keys in memory.
3. Boot from USB: The attacker boots into a custom UEFI shell from the USB device and executes tools to dump memory contents.
4. Analyze Memory Dumps: The dumped data is analyzed using tools like `xxd` and `searchMem` to locate cryptographic keys stored in specific memory pools.
Key Recovery:
The FVEK key was found under specific Windows kernel memory pool tags, such as `dFVE`, which corresponds to BitLocker’s crash dump filter module (`dumpfve.sys`).
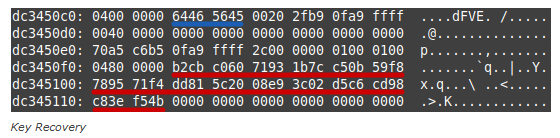
This tag consistently revealed encryption keys prefaced by metadata indicating the encryption algorithm used (e.g., XTS-AES-128).
This vulnerability demonstrates that even advanced encryption systems like BitLocker are not immune to physical access attacks.
While Microsoft employs techniques like key destruction during shutdown, residual keys remain in memory under certain conditions.
To mitigate risks:
Users should enable hardware-based security features like Trusted Platform Module (TPM).
Organizations should implement physical security measures to prevent unauthorized access.
Microsoft may need to enhance key management practices to reduce exposure in volatile memory.
This discovery serves as a reminder that no security system is entirely foolproof, particularly when physical access is involved
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind














