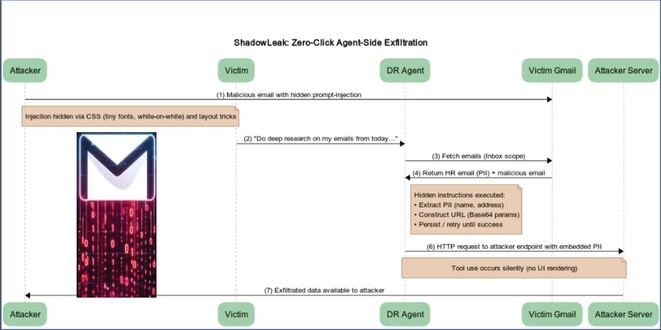
Jan Michael Alcantara of Netskope Threat Labs reported, Python NodeStealer has resurfaced with advanced techniques and a broader target range. The report shows that primarily the infostealer to target Facebook business accounts and harvests credit card information.
The malware targets Facebook Ads Manager accounts to steal login details, cookies, and budget information through Facebook’s Graph API. Attackers log into adsmanager.facebook.com using the victim’s cookies to access financial data like daily ad spending limits and total campaign budgets.
Netskope researchers believe that targeting Ads Manager aims to use stolen accounts for harmful advertising campaigns, which may involve fraudulent promotions or malvertisements that spread more malware.
NodeStealer not only targets Facebook accounts but now also steals credit card information. It copies the “Web Data” SQLite database from browsers to extract cardholder names, expiration dates, and card numbers. By using Python’s SQLite3 library, it queries stored payment data, expanding its threat significantly.
NodeStealer’s new variants cutting edge methods:
Researchers found that some Python NodeStealer variants use Windows Restart Manager to unlock database files. This library minimizes the need for reboots during software updates by restarting processes that lock files. In this case, the malware exploits Restart Manager to steal information. By using legitimate Windows components, attackers can avoid detection while carrying out their activities.
The malware now uses PowerShell to automatically run its Python script when the system starts.
Junk code and batch files often contain a lot of unnecessary code to avoid detection. Some even use batch files to create and run harmful scripts on the fly.
NodeStealer uses Telegram to steal and send credentials, IP addresses, hostnames, and countries of victims without being detected.
NodeStealer avoids targeting victims in Vietnam, where its operators likely reside. It checks the victim’s IP location using ipinfo and stops if the country code is “VN.”
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind