Over 1,200 firewall instances are vulnerable to a critical remote code execution issue, known as CVE-2024-52875. The vulnerability is found in several unauthenticated web interface paths, including /nonauth/addCertException.cs, /nonauth/guestConfirm.cs, and /nonauth/expiration.cs.
These pages do not adequately sanitize user input from the dest GET parameter, allowing attackers to inject line feed (LF) characters into HTTP responses. This vulnerability can lead to HTTP response splitting attacks, resulting in open redirects and reflected cross-site scripting (XSS).
By infosecbulletin
/ Monday , June 23 2025
A hacking group reportedly linked to Russian government has been discovered using a new phishing method that bypasses two-factor authentication...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Wednesday , June 18 2025
Russian cybersecurity experts discovered the first local data theft attacks using a modified version of legitimate near field communication (NFC)...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Tuesday , June 17 2025
Cybersecurity researcher Jeremiah Fowler discovered an unsecured database with 170,360 records belonging to a real estate company. It contained personal...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Tuesday , June 17 2025
GreyNoise found attempts to exploit CVE-2023-28771, a vulnerability in Zyxel's IKE affecting UDP port 500. The attack centers around CVE-2023-28771,...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Tuesday , June 17 2025
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has recently included two high-risk vulnerabilities in its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV)...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Monday , June 16 2025
SafetyDetectives’ Cybersecurity Team discovered a public post on a clear web forum in which a threat actor claimed to have...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Sunday , June 15 2025
WestJet, Canada's second-largest airline, is looking into a cyberattack that has affected some internal systems during its response to the...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Saturday , June 14 2025
Resecurity found 7.4 million records of Paraguayan citizens' personal information leaked on the dark web today. Last week, cybercriminals attempted...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Friday , June 13 2025
HashiCorp has revealed a critical vulnerability in its Nomad tool that may let attackers gain higher privileges by misusing the...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Friday , June 13 2025
SoftBank has disclosed that personal information of more than 137,000 mobile subscribers—covering names, addresses, and phone numbers—might have been leaked...
Read More
As of February 9, 2025, the Shadowserver Foundation reported 12,229 unpatched KerioControl instances worldwide. A heatmap from Shadowserver shows significant vulnerabilities in North America, Europe, and Asia.
The organization has identified scanning for this vulnerability in its honeypot sensors, showing that threat actors are attempting to exploit it.
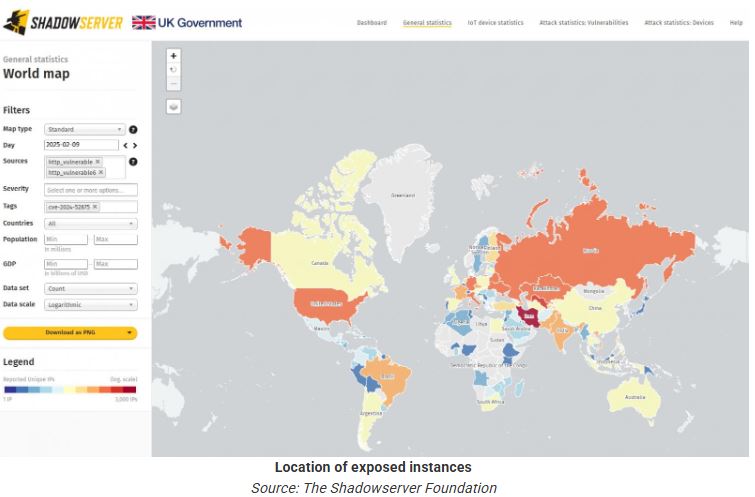
The absence of an official warning from the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) makes it harder to address risks. Organizations using these firewalls may not recognize the threat until a breach occurs or they are alerted by third-party security monitors like Shadowserver.
Unpatched KerioControl firewalls are vulnerable to attacks that allow hackers to gain full control. Exploited firewalls can become entry points for larger network intrusions or for launching additional attacks on connected systems.
In mid-December, security researcher Egidio Romano (EgiX) found the flaw that could enable risky 1-click remote code execution (RCE) attacks.
Shadowserver advises organizations to quickly assess their system vulnerabilities, monitor dashboards for alerts, and apply available patches.
KerioControl is a network security suite that small and medium-sized businesses use for VPNs, bandwidth management, reporting and monitoring, traffic filtering, AV protection, and intrusion prevention.
Apple releases update of zero-day vuln exploited in the Wild

 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind














