Malware analysts at Doctor Web have identified new versions of the NGate banking trojan. This malware steals data from the device’s NFC chip, enabling attackers to withdraw money from victims’ accounts at ATMs without their knowledge.
The NGate banker was first noticed by antivirus vendors in autumn 2023 due to attacks on major Czech banks. The attackers used social engineering, phishing, and malware to gain remote access to victims’ payment NFC capabilities. While Czech law enforcement managed to halt this campaign, the method was later adapted for illegal use in Russia.
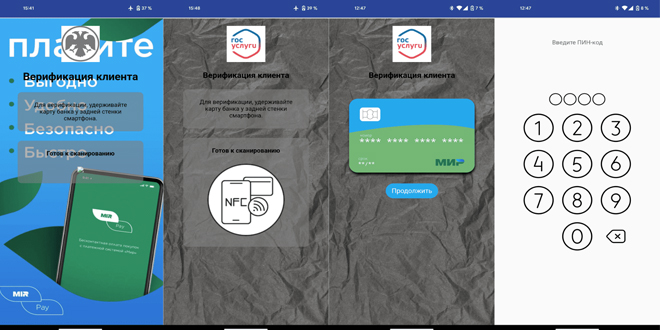
Fraudsters often start their attack with a phone call, claiming the victim is eligible for social benefits or financial gain. To receive it, the victim is instructed to click a link that leads to a fake website. This site hosts a malicious APK disguised as an app for the Gosuslugi portal, the Bank of Russia, or other popular banks, containing the NGate trojan.
The NGate banking trojan is a malicious version of the open-source NFCGate app, originally designed for debugging NFC data transfers. Attackers exploit its ability to capture NFC traffic and send it to a remote device, like a server or their own phone. They’ve altered the code to include a user interface resembling official apps and activated NFC data relay. Additionally, the app incorporates the nfc-card-reader library, allowing hackers to remotely access card numbers and expiry dates.
Once the user opens the fake application, they are asked to place their payment card on the back of the smartphone, enter their PIN, and wait for verification. During this process, all card information is collected and sent to the criminals. No rooting of the smartphone is required to access NFC data.
The attacker can steal a victim’s bank card information by holding their smartphone near the victim’s card while requesting cash from an ATM or making a contactless payment. The hacker taps their phone to transmit the victim’s card details, using the PIN the victim previously entered to confirm the transaction.
To prevent money theft, “Doctor Web” analysts recommend:
do not share your PIN or CVV codes for your bank cards,
use an antivirus program, it will block downloading and installation of malicious applications,
carefully check the addresses of web pages that ask for financial information,
only install applications from official sources such as AppGallery and Google Play,
do not talk to scammers. If you receive an unexpected call from the police, a bank or any other organization, simply hang up. If you have any doubts about the legitimacy of the call, find the contact details on the official website and contact the organization yourself.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind