The Cicada3301 ransomware is made in Rust and attacks Windows and Linux/ESXi hosts. Truesec researchers examined a version that targets VMware ESXi systems, which seems to be a variant of the same malware for Windows.
Experts mentioned that although many ransomware groups are now targeting ESXi systems, only a few, like the inactive BlackCat/ALPHV group, have used Rust-based ransomware. Analysis shows notable similarities between Cicada3301’s ransomware and ALPHV’s ransomware.
Cicada3301 is a new RaaS operation that has appeared recently. The group has already listed 23 victims on its extortion portal since mid-June. The gang published the list of victims on its Dark Web leak site.
“The Cicada3301 ransomware has several interesting similarities to the ALPHV ransomware.” reported Truesec.
Both are written in Rust
Both use ChaCha20 for encryption
Both use almost identical commands to shutdown VM and remove snapshots[1]
Both use –ui command parameters to provide a graphic output on encryption
Both use the same convention for naming files, but changing “RECOVER-“ransomware extension”-FILES.txt” to “RECOVER-“ransomware extension”-DATA.txt”[2]
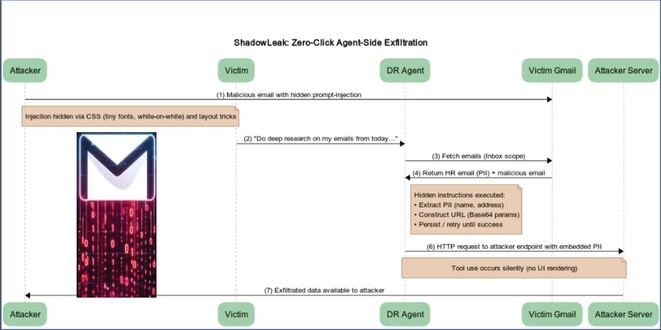
How the key parameter is used to decrypt the ransomware note
Cicada3301 attacked by using stolen or brute-forced credentials to log in through ScreenConnect. The IP address used is connected to the Brutus botnet, which may suggest a link between the two. This happened when BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware group seemed to disappear, which raises the possibility that Cicada3301 could be a rebranding of ALPHV, a collaboration with its developers, or a separate group using modified ALPHV code.
The Cicada3301 ransomware supports multiple configurable parameters that operators can use to alter its behavior during the execution. These parameters, managed via the clap::args library, include options like:
sleep: Delays execution of the ransomware by a specified number of seconds.
ui: Displays real-time progress and statistics of the encryption process, such as the number of files encrypted.
no_vm_ss: Encrypts files on ESXi hosts without shutting down running virtual machines, using the esxicli terminal and deleting snapshots.
These features make the ransomware more flexible and potentially more effective in various situations.
The Cicada3301 ransomware uses a random number generator called OsRng to create a key for encryption. It then uses a function called encrypt_file to encrypt files. This function involves extracting a public PGP key from the ransomware’s data section, which is used to encrypt the generated key.
The malware creates a note called “RECOVER-[encrypted file ending]-DATA.txt” in each folder with encrypted files. It encrypts specific file types, like documents and pictures, indicating it was first designed for Windows systems before being changed for ESXi hosts.
“After the encryption is done, the ransomware encrypts the ChaCha20 key with the provided RSA key and finally writes the extension to the encrypted file. Adding the encryption file extension The file extension is also added to the end of the encrypted file together with the RSA encrypted ChaCha20 key.” concludes the analysis that includes YARA Rule for this version of the malware.
Source: securityaffairs.com
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind