CYFIRMA analysis reveals a sophisticated malware campaign that exploits a major Indian bank’s brand through fake mobile apps. These apps, distributed via phishing links and social engineering, closely resemble the real bank apps, deceiving users into sharing their credentials and personal information. The malware uses advanced techniques, such as encrypted communication with C2 servers and altering its behavior, allowing it to evade detection by security systems.
The attackers aim to profit by stealing credentials, making unauthorized transactions, and selling stolen banking and personal data on darknet forums. This campaign may also help them set up larger fraud operations, allowing for money laundering, identity theft, and further exploitation of compromised accounts.
FinStealer malware employs advanced evasion methods to evade security systems. It uses encrypted communication with Command-and-Control servers, executes dynamic payloads, and alters its behavior during runtime. It also utilizes XOR encryption and Telegram bots for added complexity and data theft.
Attackers exploit vulnerabilities like SQL injection (CVE-2011-2688) to compromise command and control servers, gaining unauthorized access to critical information such as server passwords.
Once installed on a device, the malware gains permission to access SMS messages, allowing it to intercept one-time passwords (OTPs) and other sensitive information. This enables attackers to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA), leading to unauthorized transactions and identity theft. Its undetected nature highlights its sophistication, posing serious risks to individual users and financial institutions.
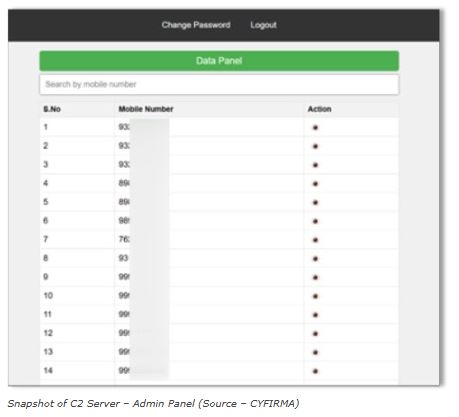
Cyfirma researchers found that malware is linked to a fake website that hosts counterfeit versions of a bank’s app. This site spreads malware through phishing campaigns disguised as ads or download prompts. The campaign highlights vulnerabilities in mobile banking systems, especially in areas with high use of digital financial services.
The malware uses a Telegram bot to send sensitive data to its command and control server including:
Banking credentials
Credit card details
Personal identification information
Security researchers also discovered a critical vulnerability (CVE-2011-2688) in the C2 server, allowing SQL injection attacks through the mysql/mysql-auth.pl script in the mod_authnz_external module.
CYFIRMA recommends using advanced endpoint protection, monitoring for suspicious behavior, regularly auditing mobile apps, and blocking known malicious indicators to safeguard against threats.
India to launch new domain name for banks to combat digital fraud
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind














