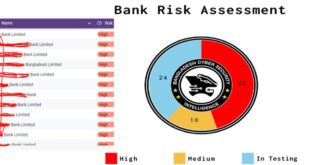
Researchers discovered a new Android banking trojan aimed at Indian users. This malware pretends to be essential utility services to deceive users into sharing sensitive information.
The malware has compromised 419 devices, intercepted 4,918 SMS messages, and stolen 623 banking credentials. The ongoing campaign is expected to affect more devices and result in more stolen data.
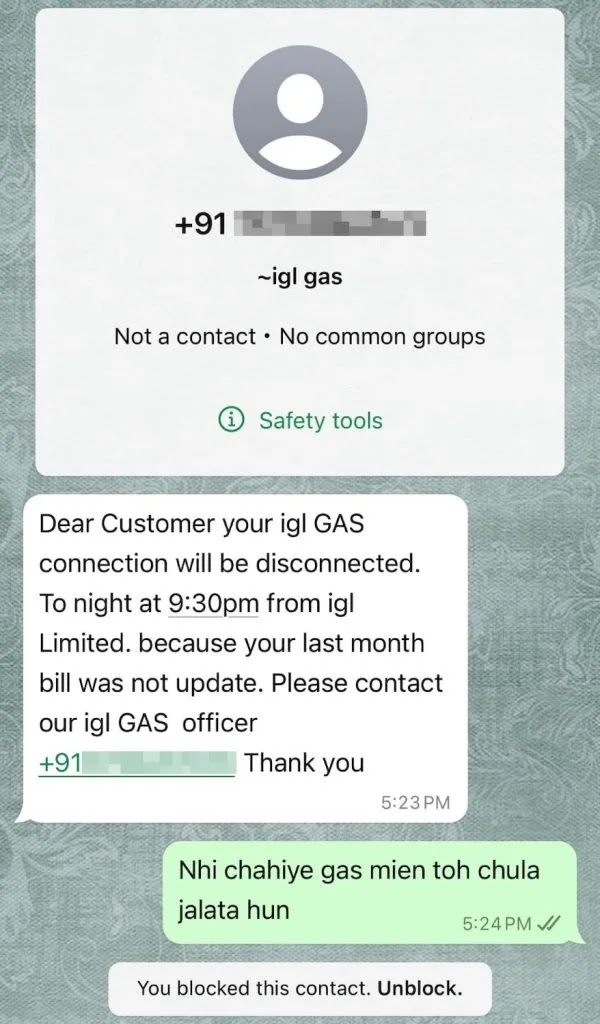
Cybercriminals are using WhatsApp’s large user base in India to share harmful APKs that, when installed, give them access to victims’ financial information.
The malware creator has developed a mobile app to manage the C2 infrastructure directly, bypassing web interfaces and communicating straight with C2 servers, unlike earlier malware.
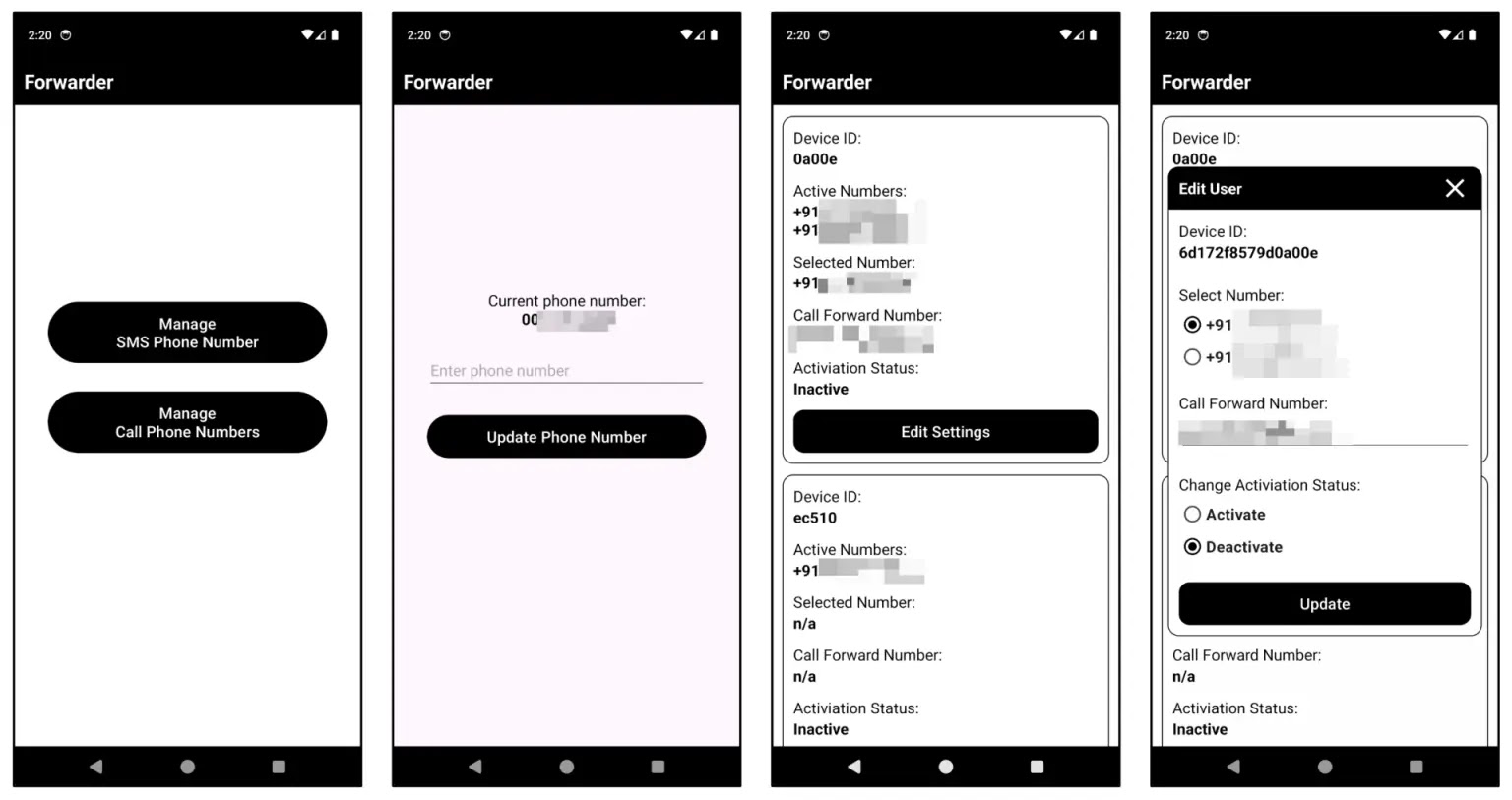
The app can remotely instruct infected devices to send SMS messages to certain numbers. It uses Firebase Realtime Database for easy storage and retrieval of configuration data, emphasizing direct device control and data extraction.
McAfee research has identified 419 unique devices infected with a specific malware variant, which is expected to rise due to the continuous evolution and spread of new strains.
The malware poses as a gas bill payment app and uses the PayRup logo to trick users into trusting it.
Phishers use the trust associated with messaging platforms to trick users into downloading harmful software, risking financial loss and personal information theft.
After installation and granting permissions, the app requests sensitive financial information like card and bank details, which it sends to a C2 server while showing a fake payment failure message.

Investigators found 5,558 records in the database, including 4,918 SMS messages and 623 financial records. Analysis of package names indicates a complex scam targeting financial institutions and utility services.
Eight unique package prefixes were identified, each linked to specific scam themes involving major banks like Axis, ICICI, and Punjab National Bank, along with regional banks and utility providers.
Due to the rise of scams on messaging platforms like WhatsApp, users should be cautious with messages from unknown sources and use strong security software to protect against threats.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind