CloudSEK’s dedicated research team delves deep into the layers of complexity to uncover a story of financial manipulation. In this comprehensive report, CloudSEK explore a money laundering scheme that exploits India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), revealing a web of deceit with real consequences for unsuspecting victims.
Scammers are using illegal instant loan apps to lure thousands of victims with false promises of substantial loans and easy repayments. They then vanish after extracting personal information and fees. These scammers are evading actions by law enforcement agencies by using Chinese payment gateways and Indian money mules.
Key Findings:
The investigation, initiated on September 8, 2023, began when CloudSEK discovered cybercriminals advertising a malicious app impersonating a prominent bank headquartered in Tamil Nadu, India, with reported revenue of $23 million USD according to ZoomInfo.
The fraudulent domain name of the identified Command and Control (C2) server consistently followed a pattern of [BANKNAME].online. (For More Information, Read Full Report)
Sensitive sources have revealed the following key insights about this alarming campaign:
- From July to September 2023, cybercriminals amassed approximately INR 37 lakhs by posing as a bank through fraudulent Chinese payment gateways.
- More than 55 harmful Android apps have been distributed through various channels.
- CloudSEK has identified over 15 payment gateways operated by Chinese individuals involved in this fraudulent scheme.
- In the aftermath of the Enforcement Directorate’s actions against legitimate payment gateways for money laundering in September 2022, cybercriminals have shifted to using in-house or small-scale legal/illegal payment gateways.
- Scammers employ increasingly sophisticated methods to evade law enforcement, highlighting the importance of organizations and regulators staying vigilant and implementing robust safeguards.
Statistics from the Fraud Campaign (July 22, 2023 – September 18, 2023):
- Unchecked Total Stolen Amount: Approximately INR 37 lakhs
- Unchecked Malicious Android Apps: Over 55
- Unchecked The Chinese individuals are operating these fraud payment gateways in multiple countries including Indonesia, Malaysia, South Africa, Mexico, Brazil, Turkey, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Colombia.
Modus Operandi:
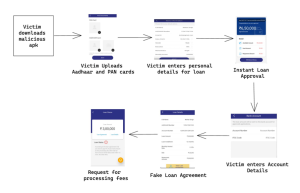
The scammers employ a multi-step approach:
Creation of Fake Instant Loan Apps:
Scammers develop counterfeit instant loan apps and make them available on app stores or third-party websites.
Promoting Illicit Apps:
Scammers aggressively advertise illegal loan apps, enticing victims with promises of substantial loans and convenient repayment terms.
Solicitation of Personal Information:
Once the app is downloaded, victims are coerced into providing personal details, including their name, address, phone number, and bank account information.
Permission Access and Processing Fee Payment:
The app requests permission to access the victim’s contacts and other phone data. Subsequently, victims are coerced into paying a processing fee, typically 5% of the promised loan amount.
Disappearance after Payment:
Once the processing fee is paid, the scammers vanish, leaving victims without the promised loan funds.
“A notable trend we’ve observed is scammers exploiting Chinese payment gateways due to their relative ease of use and limited regulatory scrutiny. These gateways offer a convenient bridge to funnel funds outside India, leveraging sophisticated techniques that blur jurisdictional lines, making it challenging to track and intercept the money trail. This enables scammers to sidestep the legal and financial roadblocks, making it imperative for authorities to enhance cooperation and adopt advanced measures to counter this sophisticated threat.” said Sparsh Kulshrestha, Senior Security Analyst at CloudSEK
Following the Money: How Chinese Payment Gateways Facilitate Fake App Loan Scams:
Creation of Fraudulent Payment Gateways:
Scammers operate fraudulent payment gateways primarily hosted in China. These gateways exploit the Unified Payments Interface’s (UPI) QR code feature, redirecting victims to legitimate UPI apps like PhonePe and GPay.
Recruitment of Individuals as Money Mules:
The scammers recruit individuals via Telegram, offering them a commission to provide their bank accounts.
Transfer of Funds To Mule Accounts:
These recruits are instructed to change the associated mobile numbers with banks, granting the scammers full remote control over the accounts. These compromised bank accounts are then used to receive payments from victims through the fraudulent payment gateways.
Money Laundering Process:
Scammers receive payments from victims through fraudulent payment gateways, utilizing hawala and fei-chien for money laundering—a challenging-to-track alternative remittance system.
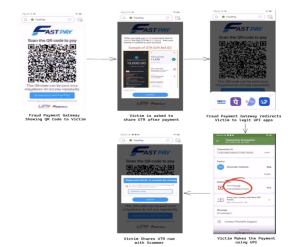
CloudSEK urges all stakeholders, including financial institutions, regulatory authorities, and law enforcement agencies, to remain vigilant and work together to combat this growing threat to India’s digital payment ecosystem. This collaborative effort is essential to protect the interests and financial security of Indian citizens. CloudSEK has shared the report with CERT-In for further action.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind