Recent security research has shown that attackers can weaken zero-trust security frameworks by exploiting a key DNS vulnerability, disrupting automated secret rotation.
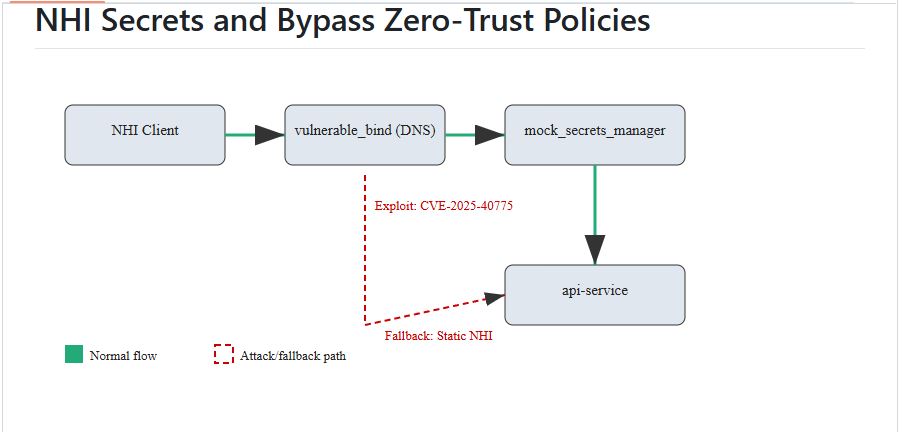
The research reveals a complex attack chain that starts with disrupting DNS servers and ends with unauthorized access to cloud services, exposing serious flaws in Non-Human Identity (NHI) management.
The demonstration focuses on CVE-2025-40775, a newly revealed denial-of-service vulnerability in BIND DNS servers versions 9.20.0 to 9.20.8.
This flaw lets remote attackers crash DNS servers by sending malformed Transaction Signature (TSIG) packets with invalid algorithm values, leading to assertion failures and service shutdown.
The vulnerability has a CVSS score of 7.5 and does not require authentication, posing a significant risk to internet-facing DNS infrastructure.
Security researcher AlexSvobo discovered a critical attack vector and created a proof-of-concept that shows how failures in DNS infrastructure can lead to bypassing zero-trust policies.
The research project, available as an open-source repository, offers a controlled cloud-native lab environment that simulates real-world enterprise security setups, including secrets managers, API services, and automated NHI rotation systems.
The attack uses a three-phase method that takes advantage of the interconnectedness of modern cloud security controls.
Attack Chain Workflow
Phase 1: Trigger DNS Server Crash
Goal: Disrupt DNS resolution for target cloud services.
Method: Craft malformed DNS queries exploiting a known BIND vulnerability related to TSIG records (CVE-2025-40775).
Tool: Scapy for packet generation.
Phase 2: Exploit NHI Secret Rotation Failures
Goal: Force systems to rely on static/fallback NHIs and capture them.
Method: Disrupt communication with secrets managers (e.g., HashiCorp Vault) via DNS DoS, causing secret rotation retries. Investigate if plaintext fallback secrets are transmitted during these retries, or if reliance on stale secrets creates an opportunity.
Tool: tcpdump for network capture, Python client simulation.
Phase 3: Bypass Zero-Trust Policies
Goal: Use stolen/exposed NHIs to impersonate services and exfiltrate data.
Method: Forge authentication tokens (e.g., JWTs) or directly use API keys to access restricted resources.
Tool: Python script to access protected API endpoint.
To read the full report click here.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind