In October 2023, Sekoia analysts discovered a new Adversary-in-The-Middle (AiTM) phishing kit used by several hackers for widespread attacks. This kit is linked to the Tycoon 2FA Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) platform, active since at least August 2023.
The Sekoia Threat Detection & Research (TDR) team analyzed the Tycoon 2FA PhaaS kit and shared findings on Twitter. We continue to monitor the Tycoon 2FA phishing pages, campaigns using the kit, updates to the source code, and the alleged developer’s activities.
Sekoia analysts found that the Tycoon 2FA phishing kit has become very popular, with over 1,100 related domain names detected from late October 2023 to late February 2024.
In mid-February 2024, a new version of the Tycoon 2FA was discovered. It improves its ability to avoid detection and changes the way it communicates over the network. Sekoia analyzed these updates and identified the new infrastructure. Currently, the service leverages 1,100 domains and has been observed in thousands of phishing attacks.
Tycoon 2FA attacks:
Tycoon 2FA attacks use a simpler method where the hacker sets up a fake webpage to capture a user’s login details and session information, tricking them into thinking they’re using the real service.
“Once the user completes the MFA challenge, and the authentication is successful, the server in the middle captures session cookies,” Skoia explains. This way, the attacker can replay a user’s session and bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) mechanisms.
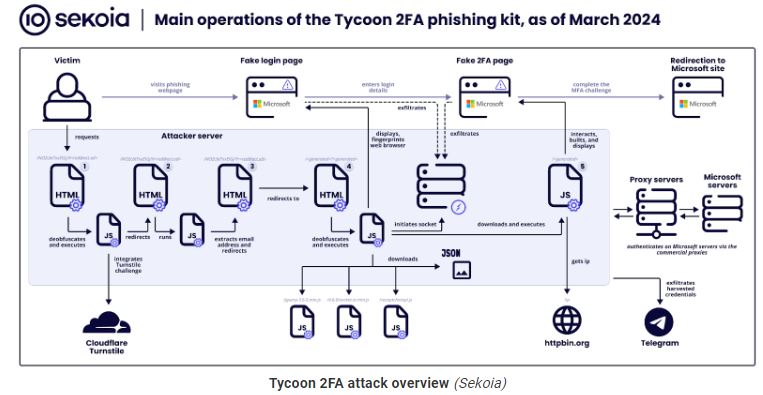
Sekoia’s report describes the attacks in seven distinct stages as described below:
Stage 0 – Attackers distribute malicious links via emails with embedded URLs or QR codes, tricking victims into accessing phishing pages.
Stage 1 – A security challenge (Cloudflare Turnstile) filters out bots, allowing only human interactions to proceed to the deceptive phishing site.
Stage 2 – Background scripts extract the victim’s email from the URL to customize the phishing attack.
Stage 3 – Users are quietly redirected to another part of the phishing site, moving them closer to the fake login page.
Stage 4 – This stage presents a fake Microsoft login page to steal credentials, using WebSockets for data exfiltration.
Stage 5 – The kit mimics a 2FA challenge, intercepting the 2FA token or response to bypass security measures.
Stage 6 – Finally, victims are directed to a legitimate-looking page, obscuring the phishing attack’s success.
The diagram below outlines the steps of the attack.
To read out the full report click here.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind