Researchers found that recently the ransomware attack on the digital payment system used by many of India’s banks started with a vulnerability in Jenkins, an open-source automation system for software developers. Juniper Networks recently published a study on the abuse of CVE-2024-23897, a vulnerability in Jenkins Command Line Interface.
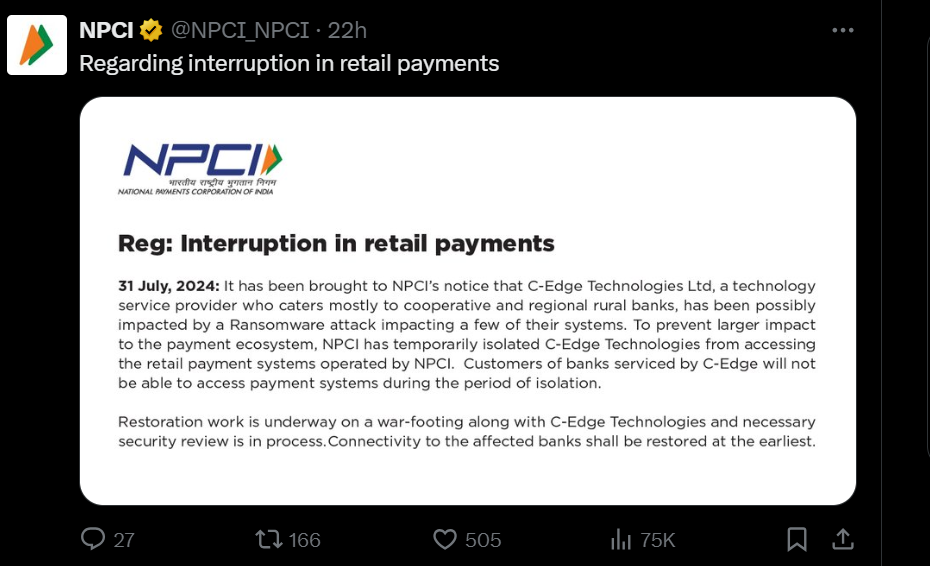
The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) announced on July 31 that it is facing a disruption due to a ransomware attack on a third-party technology provider.
Services were restored one day later, but the RansomEXX ransomware gang later claimed responsibility for the attack last week. They stated on their leak site that they stole 142 GB from a digital payment platform connected to C-Edge.
Juniper Networks analyzed a report submitted by NPCI to the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team. The researchers stated that the attack highlights the importance of promptly applying security patches and fixing server misconfigurations to prevent the exploitation of security vulnerabilities.
Analysis of the Attack:
Brontoo Technology Solutions reported to CertIn that the attack started from a misconfigured Jenkins server. Further analysis showed that the attacker used CVE-2024-23897 to access the victim’s system without permission.
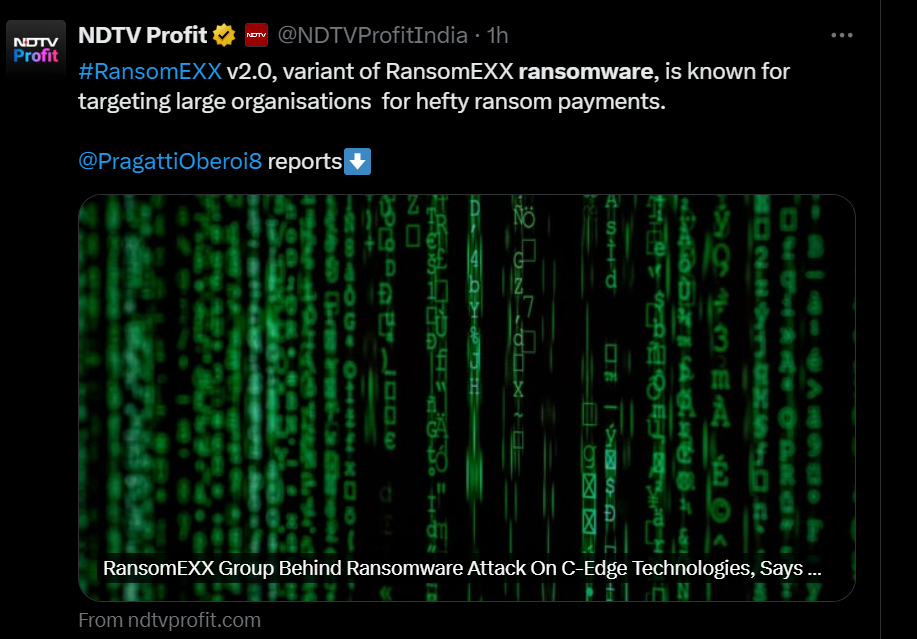
CVE-2024-23897 is a vulnerability in the Jenkins Command Line Interface, where an attacker tries to gain unauthorized access to targeted systems. The sample ransom note by this group looks like the image below:
CVE-2024-23897: In-Depth Technical Analysis
Jenkins is a free automation server that helps developers worldwide build, test, and deploy software. The vulnerability affects the Jenkins Command Line (CLI), which can be accessed using SSH, WebSocket, or HTTP via a CLI Client.
An unauthenticated user can read the first few lines of any files on the file system due to a vulnerability. This vulnerability is caused by not properly validating user-supplied strings when processing CLI commands. It exists because the command parser’s built-in feature is enabled by default. If this vulnerability is successfully exploited, sensitive files and data may be leaked, commands can be executed, and a ransomware attack can be enabled. Juniper Threat Labs will use a specific version to demonstrate this attack. Click here to read out the full report.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind