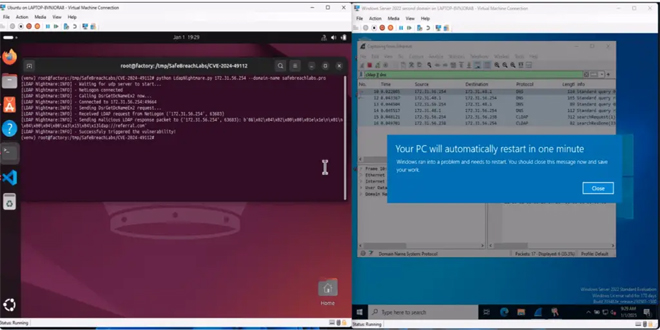
SafeBreach Labs revealed a zero-click vulnerability in the Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) service, dubbed “LDAP Nightmare”. This critical vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-49112, has been assigned a CVSS score of 9.8, highlighting its severe implications for enterprise networks.
SafeBreach researchers demonstrated how the exploit could crash unpatched Windows Servers, including the Active Directory Domain Controllers (DCs).
First disclosed on December 10, 2024, during Microsoft’s Patch Tuesday, CVE-2024-49112 is a Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability within LDAP. LDAP is integral to Microsoft’s Active Directory, facilitating directory services communication across organizational networks. “The ability to run code on a DC or to elevate users’ privileges through a DC heavily affects network security posture,” the SafeBreach Labs team emphasized.
While Microsoft acknowledged the risk, details surrounding the exploitation path remained scarce until SafeBreach’s analysis. “We decided as a team to prioritize it and are proud of the findings we have identified that will help enterprises address any potential exposures,” the researchers noted.
SafeBreach developed a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit demonstrating the CVE-2024-49112 vulnerability’s devastating effects. Their findings show that the exploit:
Requires no authentication or pre-requisites, aside from Internet connectivity for the DNS server.
Can crash unpatched Windows Servers by triggering an LSASS (Local Security Authority Subsystem Service) crash via LDAP queries.
The exploitation process involves:
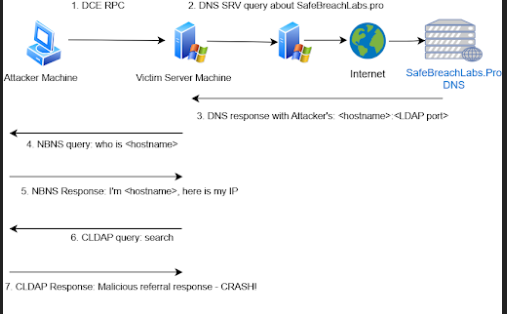
The attack flow | Source: SafeBreach Labs
- Sending a DCE/RPC request to the victim server.
- Triggering a DNS SRV query about a domain controlled by the attacker (e.g., SafeBreachLabs.pro).
- Manipulating NetBIOS and CLDAP responses to redirect the victim to the attacker’s LDAP server.
- Using a crafted LDAP referral response to crash the victim’s LSASS and force a reboot.
SafeBreach highlighted the technical in their findings: “The condition checks whether the ‘lm_referral’ value is inside the range of the ‘referral table’. In the vulnerable version without the patch, this ‘lm_referral’ value is indeed used to access a certain offset inside the referral table.”
This vulnerability affects all unpatched versions of Windows Server, from Windows Server 2019 to 2022. Exploiting it could enable adversaries to take complete control of domain resources or crash critical infrastructure.
To mitigate the risk, organizations should:
Apply Microsoft’s patch immediately. SafeBreach verified that the patch effectively prevents exploitation.
Monitor for suspicious activity, such as anomalous CLDAP referral responses, DsrGetDcNameEx2 calls, or DNS SRV queries.
SafeBreach also released a PoC tool that tests a vulnerable Windows Server against CVE-2024-49112, available on their GitHub repository.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind