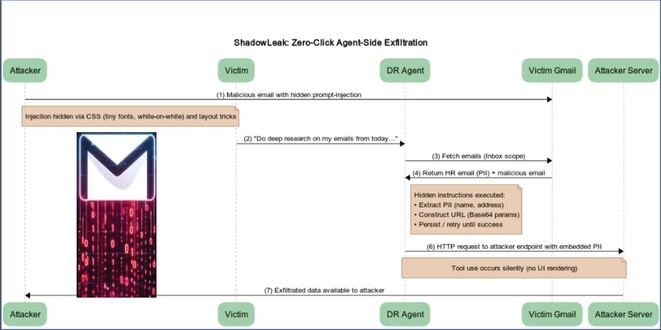
A critical security flaw in the Next.js framework, marked as CVE-2025-29927, lets attackers bypass authorization, threatening web applications. This vulnerability stems from the mishandling of the x-middleware-subrequest header in Next.js middleware, which could allow unauthorized access to sensitive admin areas and protected resources.
The vulnerability affects various versions of the React web framework, with different exploitation methods for each version. NullSecurityX reports that the core of this vulnerability lies in Next.js’s middleware processing logic, specifically how it handles the x-middleware-subrequest header.
This header was meant to stop infinite middleware loops by recognizing internal subrequests, but poor implementation lets external requests exploit it. This vulnerability is especially harmful when used with JSON Web Token (JWT) or cookie authentication, as header manipulation can bypass token validation completely.
Security researchers have created simple scripts that test common admin paths (/admin, /dashboard, /settings) with the malicious header to find vulnerabilities in applications.
The vulnerability goes beyond just bypassing authorization. In apps that depend only on Next.js middleware for security, attackers could access sensitive user data, change app settings, or perform admin tasks without proper authentication.
Organizations using Next.js should quickly review their middleware and apply any security patches.
This discovery emphasizes the importance of defense-in-depth security strategies, utilizing authorization controls at various application layers instead of just relying on middleware protections.
HashiCorp has released a security advisory for a new vulnerability in Vault, its popular secrets management platform. Known as CVE-2025-6203 and rated CVSS 7.5 (High), this flaw could enable a malicious user to cause a Denial-of-Service (DoS) by sending specially crafted JSON payloads.
The issue stems from Vault’s handling of complex JSON requests. According to the advisory, “A malicious user may submit a specially-crafted complex payload that otherwise meets the default request size limit which results in excessive memory and CPU consumption of Vault. This may lead to a timeout in Vault’s auditing subroutine, potentially resulting in the Vault server to become unresponsive.”
ChatGPT Leaks: 1,000 Public AI Conversations Analyzed: What research find
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind