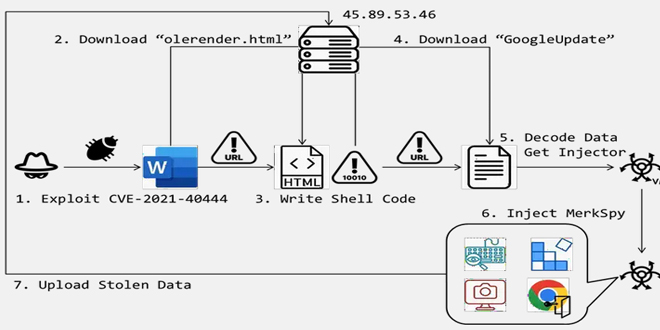
FortiGuard Labs found an attack that uses the CVE-2021-40444 vulnerability in Microsoft Office. This flaw lets attackers run harmful code through specific documents. The attack deployed a spyware called “MerkSpy” which secretly watches user activities, collects sensitive information, and stays on compromised systems.
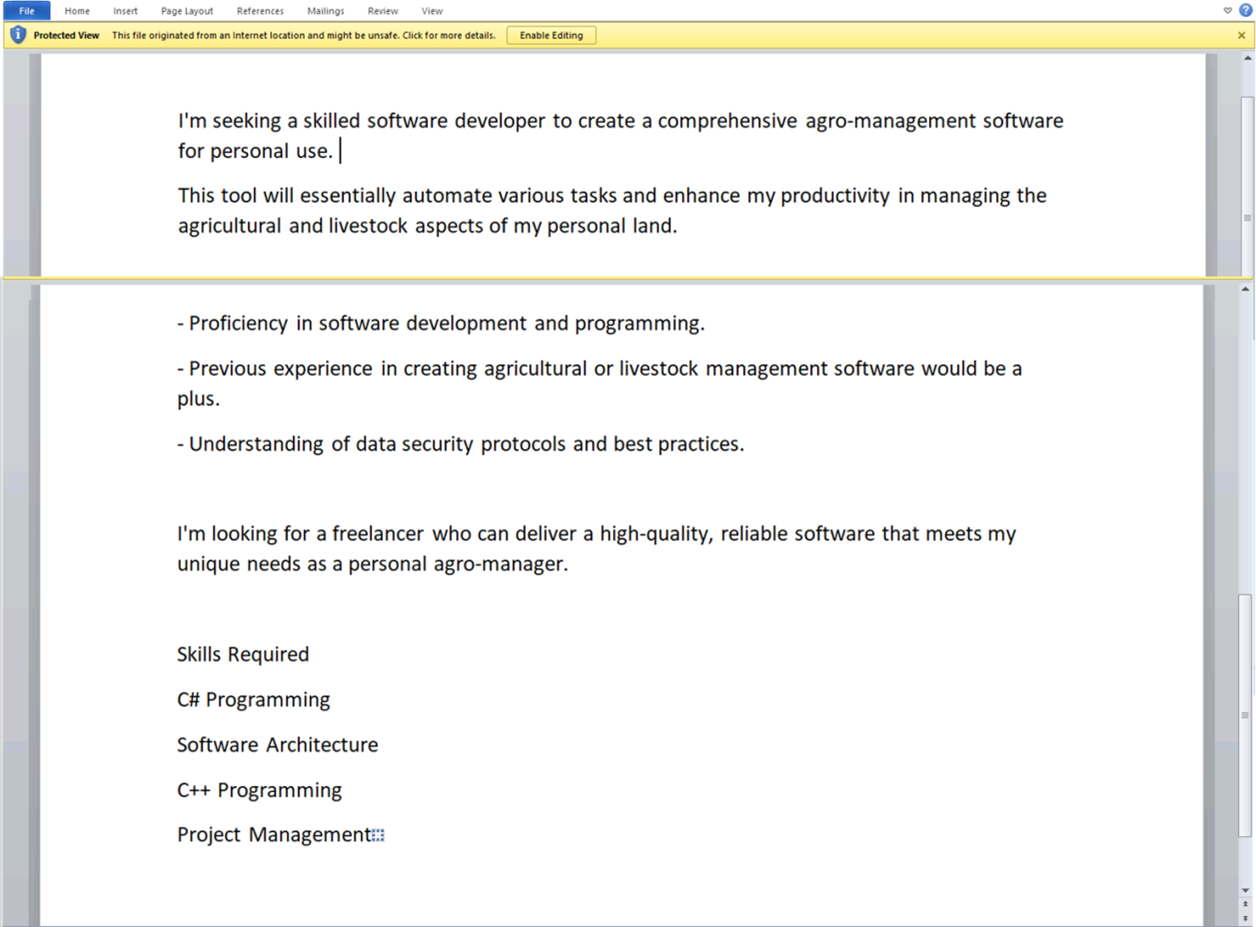
The attack starts with a harmless-looking Microsoft Word document, usually pretending to be a job posting or something else interesting. When the document is opened, it triggers a vulnerability (CVE-2021-40444) that lets the attackers run harmful code and download more harmful software.
After being successfully exploited, the malicious document activates a downloaded file called “olerender.html” from a remote server. This HTML file contains a harmless script at the beginning to hide its true purpose, and the latter part contains the harmful code and injection process, which is used to carry out the attack on the victim’s computer.
The “olerender.html” file checks the operating system’s version and extracts the appropriate shellcode based on whether it detects an X64 architecture. After determining the OS version and extracting the shellcode, “olerender.html” retrieves the Windows APIs “VirtualProtect” and “CreateThread.” These functions are essential for the next steps. “VirtualProtect” changes memory permissions to securely write the decoded shellcode into memory, while “CreateThread” executes the injected shellcode, preparing for the download of the next payload from the attacker’s server.
MerkSpy is a powerful tool used by cybercriminals to record keystrokes, take screenshots, and steal login information from web browsers like Chrome. This stolen data is sent to the attackers, putting personal and financial information at risk.
“This shellcode decodes the downloaded content to execute an injector responsible for loading the MerkSpy spyware into memory and integrating it with active system processes,” said Cara Lin, a senior researcher at FortiGuard Labs. “MerkSpy is capable of sophisticated surveillance activities, including keystroke logging, screenshot capture, and harvesting Chrome browser login data.“
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind