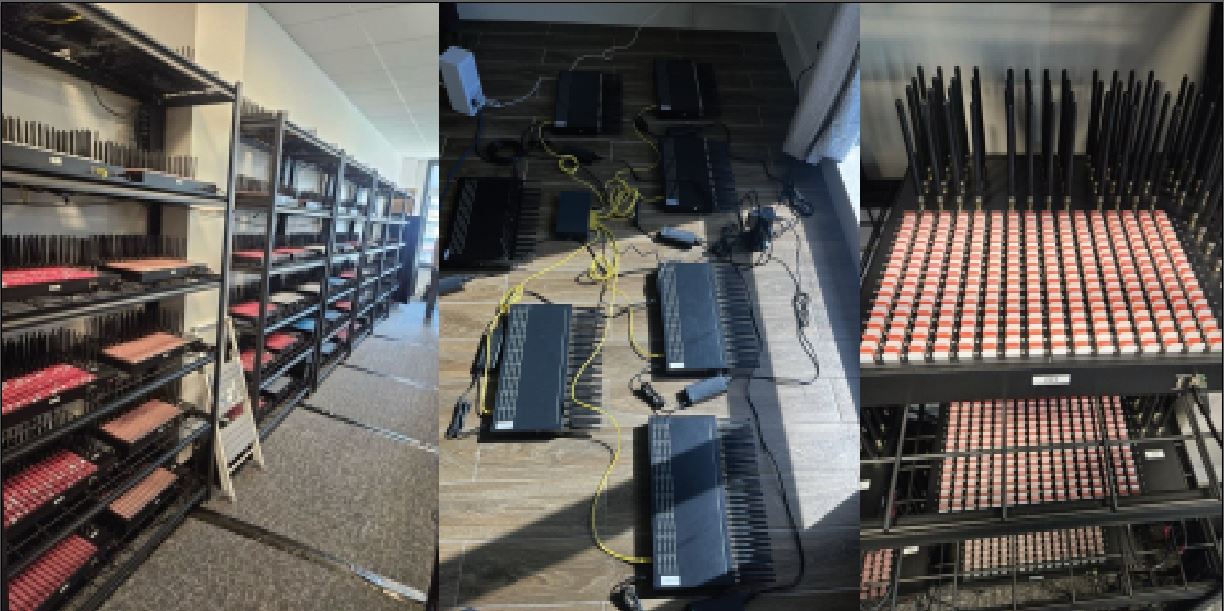
SafetyDetectives researchers found that Microsoft Defender was tricked by malware which allowed cryptocurrency theft from a user while analyzing a misleading NFT game app that aimed to steal cryptocurrency.
The application bypassed Google’s two-factor authentication, compromising the device and stealing over $24,000 in cryptocurrency.
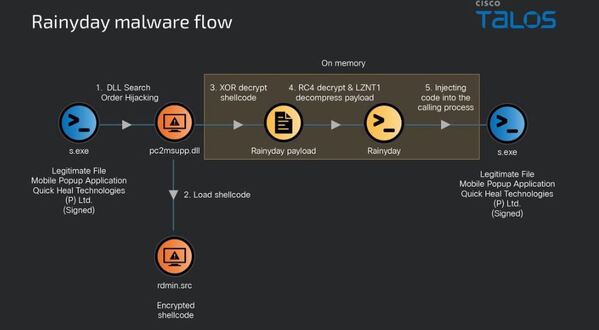
Researchers have found that this malware works silently in the background, collecting sensitive information and potentially taking over the user’s Google account, even if it’s protected by two-factor authentication (2FA). It does this by installing a harmful Chrome extension that looks like Google Keep, allowing it to bypass 2FA.
The SafetyDetectives team tested Microsoft Defender against a malware-infected app, using Wireshark to track network traffic and locate the malware.
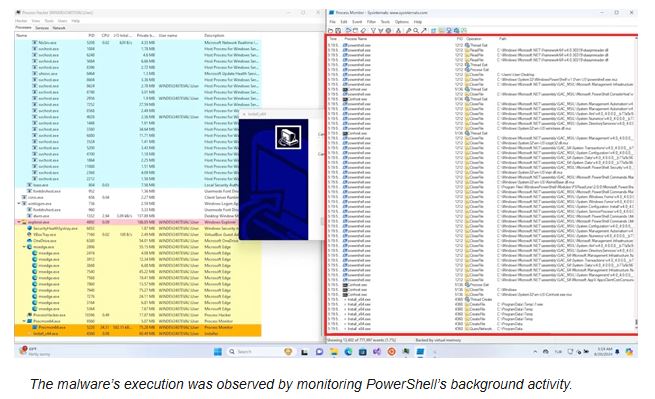
The research team found that Microsoft Defender did not prevent the virus from installing and running, which allowed the malware to access system operations, download suspicious files, gather sensitive information, and track the user’s location.
The team found that the malware was designed to deactivate if the user was in Russia, Ukraine, or Belarus, likely because of its origin. The fake Chrome extension allowed the malware to track visited websites, steal login information, and monitor copied content. It gathered everything needed to take remote control of the system, and Microsoft Defender failed to issue a warning.
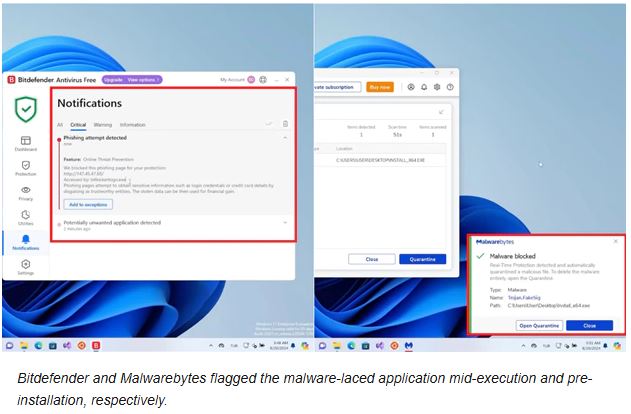
While testing Bitdefender,The antivirus couldn’t stop the installation right away, but it did act just as the malware tried to reach important information like browsing history, cookies, and login details.
Malwarebytes effectively prevented the attack in the last test by flagging the malicious app installation.
“While Malwarebytes stopped the breach faster than Bitdefender, neither is inherently better in dealing with this specific malware, as both were able to prevent critical compromise. Bitdefender may even have the benefit of having fewer false positives,” the researcher said.
SafetyDetectives’ Research Team emphasizes the need for strong antivirus software to prevent malware and advises caution when downloading unverified apps online.
Source: safetydetectives, Hackread
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind