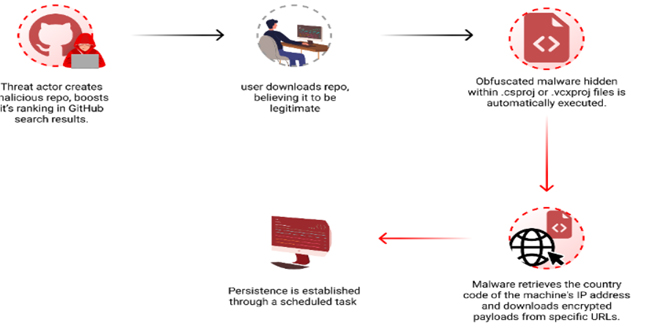
Checkmarx researchers found that hackers are using GitHub search results to distribute long-lasting malware to developers’ computers. The attackers in this campaign make harmful repositories with popular names and topics. They use techniques like automated updates and fake stars to improve search rankings.
“By leveraging GitHub Actions, the attackers automatically update the repositories at a very high frequency by modifying a file, usually called “log”, with the current date and time or just some random small change. This continuous activity artificially boosts the repositories’ visibility, especially for instances where users filter their results by “most recently updated,” increasing the likelihood of unsuspecting users finding and accessing them.” reads the report published by Checkmarx. “While automatic updates help, the attackers combine another technique to amplify the effectiveness of their repo making it to the top results. The attackers employed multiple fake accounts to add bogus stars, creating an illusion of popularity and trustworthiness.”
To avoid detection, hackers hid the harmful code in Visual Studio project files (.csproj or .vcxproj), which is automatically run during project compilation.
GitHub malware:
The researchers noticed that the payload is delivered based on the victim’s origin, and is not distributed to users in Russia. In the recent campaign, the attackers used a large, padded executable file that is similar to the “Keyzetsu clipper” malware.
The new malware campaign is similar to the “Keyzetsu clipper” malware and targets cryptocurrency wallets. On April 3rd, the attacker updated their code and linked it to a different URL. The URL downloads an encrypted .7z file that contains an executable called feedbackAPI.exe.
The attackers added many zeros to the executable file to make it bigger than the limit of security solutions like VirusTotal. This makes it impossible to scan the file. The malware maintains persistence by creating a scheduled task that runs the executable every day at 4AM without user confirmation.
“The use of malicious GitHub repositories to distribute malware is an ongoing trend that poses a significant threat to the open-source ecosystem. By exploiting GitHub’s search functionality and manipulating repository properties, attackers can lure unsuspecting users into downloading and executing malicious code.” concludes the report. “These incidents highlight the necessity for manual code reviews or the use of specialized tools that perform thorough code inspections for malware. Merely checking for known vulnerabilities is insufficient.“
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind