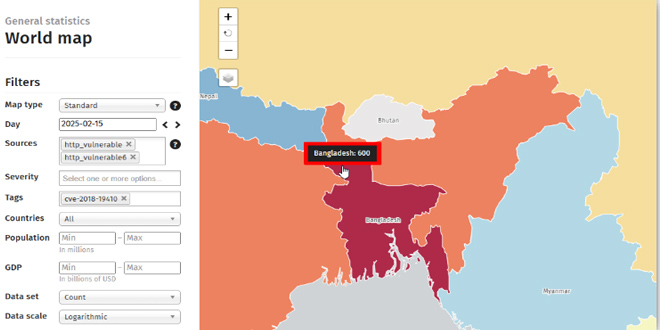
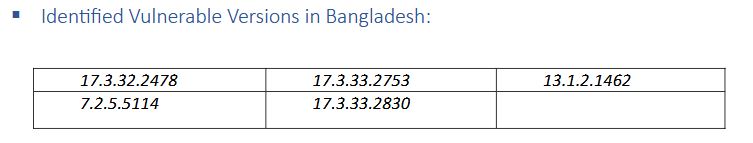
The Cyber Threat Intelligence Unit of BGD e-GOV CIRT has found 600 vulnerable PRTG instances in Bangladesh, affected by the critical CVE-2018-19410 vulnerability. This flaw allows remote, unauthenticated attackers to create admin users, risking unauthorized access and data breaches. It primarily impacts PRTG Network Monitor versions prior to 18.2.40.1683 and is actively exploited by cybercriminals. Immediate action is necessary to mitigate this serious threat.
Vulnerability Details:
# CVE ID: CVE-2018-19410
#CVE Type: Authentication Bypass, Improper Authorization, Local File Inclusion (LFI)
# Severity: 9.8 Critical
# Attack Vector: Remote
# Exploitability: Unauthenticated remote attackers can create users with admin
privileges
Affected Software:
# Software: PRTG Network Monitor
# Affected Versions: earlier than 18.2.40.1683
Attack Method:
# The flaw exists in /public/login.htm, where an attacker can override attributes of the
‘include’ directive.
# Attackers can include /api/addusers in the request, allowing unauthorized user
creation with read-write (admin) privileges.
# This leads to authentication bypass, improper authorization, and file inclusion attacks.
Potential Impact:
Unauthorized attackers fully compromised the system.
Malicious users gained privileged access.
Arbitrary code was executed through unauthorized file inclusion.
Data was stolen, causing disruptions in affected networks.
Bangladesh among the Most Affected Countries:
A significant number of 600 vulnerable instances have been detected in Bangladesh, running
outdated PRTG versions
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs):
# Suspicious Logs:
– Unusual requests to /public/login.htm
– Unauthorized execution of /api/addusers
– Unexpected admin account creation in PRTG logs
# File System Changes:
– Unauthorized user account modifications/creation
– Unexpected configuration changes in the PRTG system
# Network Anomalies:
– High-volume HTTP requests targeting PRTG login pages
– Unauthorized administrative actions from unknown IP addresses
Check for Indicators of Compromise (IoCs):
Review PRTG logs for unauthorized account creations and check for suspicious logins and file changes.
Limit access to the PRTG web interface to trusted internal networks.
Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for admin accounts.
Use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to identify suspicious activity and monitor SIEM alerts for unusual user behavior.
Network Segmentation:
# Isolate PRTG servers from internet exposure where possible.
Malware campaign target Bangladeshi Government Entities: Report
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind