Bangladesh Cyber Security Intelligence (BCSI) has published Financial Threat Assessment report for 2024. In an era where financial institutions and Critical Information Infrastructure (CII) are essential to both economic and national stability, the growing frequency and complexity of cyber threats have underscored a pressing truth: Bangladesh’s national security is under significant threat.
The financial sector in Bangladesh, especially its banks, is increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks due to outdated practices and systemic weaknesses. Research by NVDP, CS-CERT, and BCSI Threat Intelligence indicates that most banks are at high risks for cyber attack. Threat intelligence from dark web forums, hacking communities, and underground marketplaces has uncovered alarming trends that expose significant gaps in cybersecurity practices.
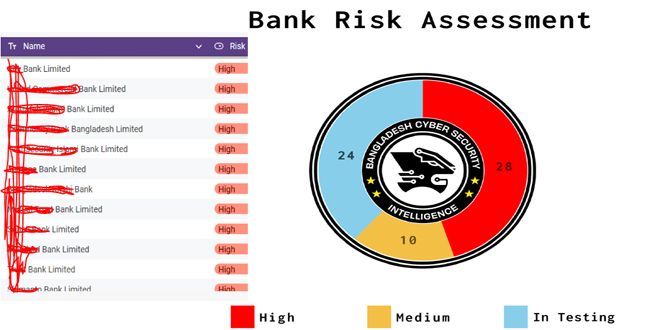
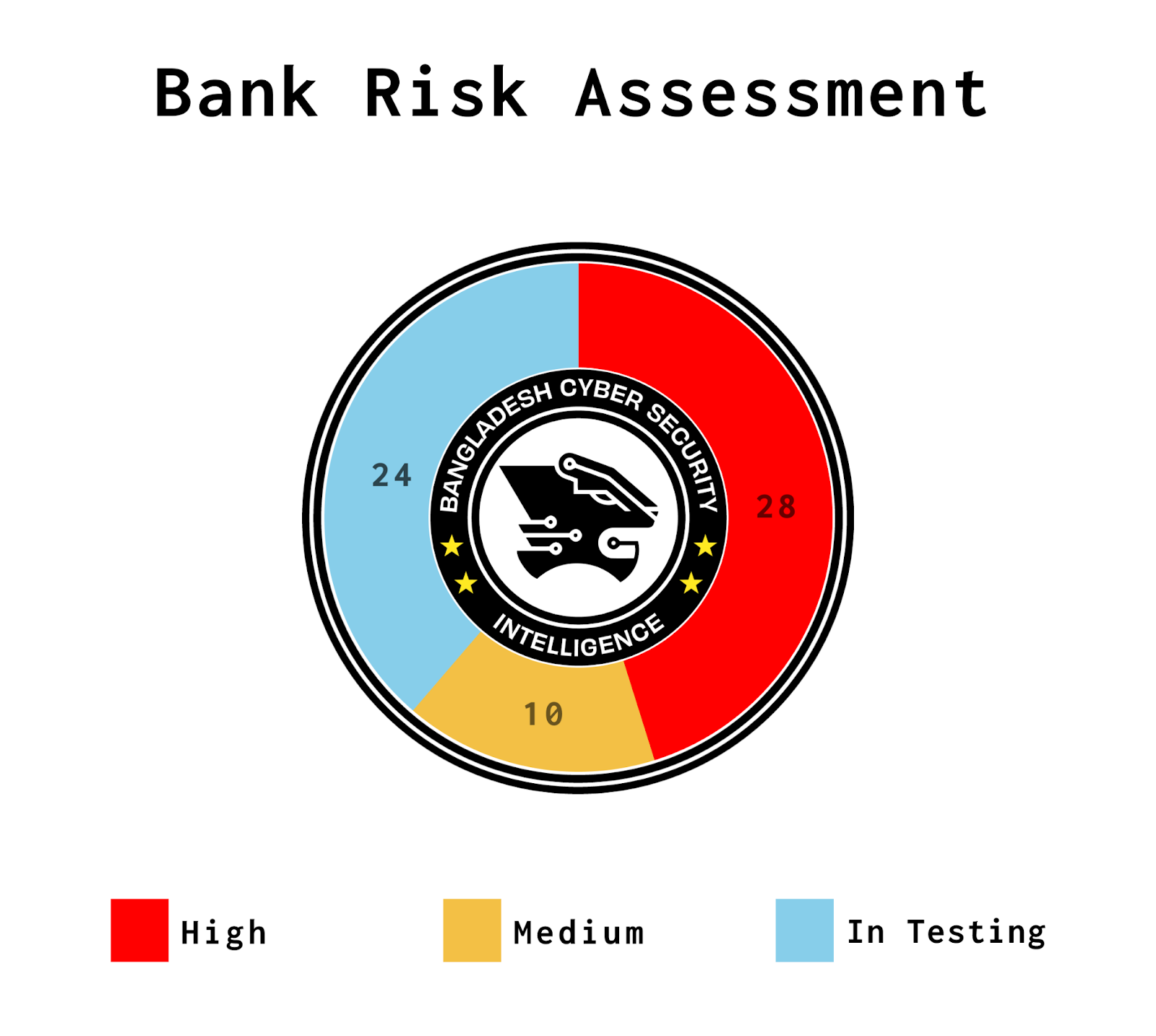
According to the report, BCSI marks Bangladeshi 28 banks high, 10 medium for cyber attack while 24 banks status are in testing.
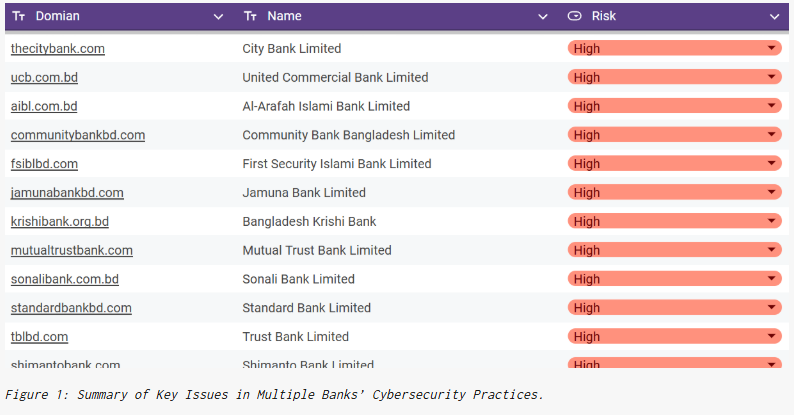
“Out of 62 banks, 38 have completed their tests, while 24 are still in the testing phase. The following image will provide a summary of key issues affecting multiple banks, highlighting both institution-specific vulnerabilities and broader systemic challenges.”
Cause Analysis:
Conflict of Interest and Corruption within IT Teams:
A troubling trend has emerged where IT staff in banks engage in unethical behavior, accepting kickbacks or percentages in exchange for awarding contracts to cybersecurity companies offering Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) services. This conflict of interest severely undermines the effectiveness of cybersecurity measures and exposes financial institutions to greater risk of cyberattacks.
Exploitation of Higher Authority References:
Many cybersecurity firms bypass fair procurement processes by leveraging personal or political ties with high-ranking officials. This practice often leads to subpar services being provided while more qualified firms, lacking such connections, are overlooked. The result is an inefficient system that hinders the adoption of innovative and effective cybersecurity solutions.
Tender Manipulation by Cybersecurity Firms:
Investigations have uncovered that some cybersecurity firms operate multiple proxy companies to submit bids for the same tenders. This creates a false appearance of competition while ensuring that contracts are awarded to one of their own controlled entities. Such manipulative tactics erode trust in the tendering process and often result in the selection of companies lacking the necessary expertise for effective security assessments and penetration testing.
Reliance on Low-Level Certifications:
A significant number of IT staff in banks hold entry-level certifications, such as Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), which offer limited practical value in addressing complex cybersecurity challenges. Relying on these basic credentials, rather than evaluating actual skill and experience, weakens the sector’s ability to defend against sophisticated cyber threats.
Shortage of Skilled Professionals:
Both bank IT teams and local cybersecurity firms are facing a critical shortage of skilled professionals. This talent gap leads to an overreliance on automated tools and basic frameworks that are insufficient for defending against advanced cyberattacks. Without significant investment in workforce development and training, these vulnerabilities will persist and worsen.
Use of Unauthorized or Cracked Tools:
Several banks have been found using unauthorized or cracked versions of vulnerability scanning tools. These tools are often unreliable, producing inaccurate results, and can introduce new security risks, compounding the vulnerabilities they are meant to mitigate.
Corruption and Unethical Practices:
Corruption continues to plague the cybersecurity industry, with some firms using personal connections and unethical practices to secure contracts. This results in the provision of low-quality VAPT services, leaving banks with inadequate security assessments that fail to identify critical vulnerabilities, further exposing them to cyber threats.
BCSI reached the affected entities but no response has been received, and It warns to publish a detailed report if proper action is not taken.
The Financial Threat Assessment 2024 underscores the urgent need to improve the cybersecurity of Bangladesh’s financial institutions and Critical Information Infrastructure (CII). Systemic vulnerabilities, unethical practices, and a shortage of skilled professionals have exposed these sectors to increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, threatening national security and economic stability.
While BCSI has assessed some organizations, many others remain untested, and the full scope of vulnerabilities will only be clear once these assessments are completed. A comprehensive CII Security Report, detailing vulnerabilities, challenges, and recommendations for strengthening security, will be published once all evaluations are finalized.
BCSI recently launched National Vulnerability Discloser Program (NVDP) to serve as a centralized platform for security researchers to responsibly disclose vulnerabilities they discover in the systems and applications deployed across various government entities. By establishing a clear and transparent process for reporting vulnerabilities, the NVDP facilitates timely mitigation efforts, reducing the risk of exploitation and enhancing overall cybersecurity resilience.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind