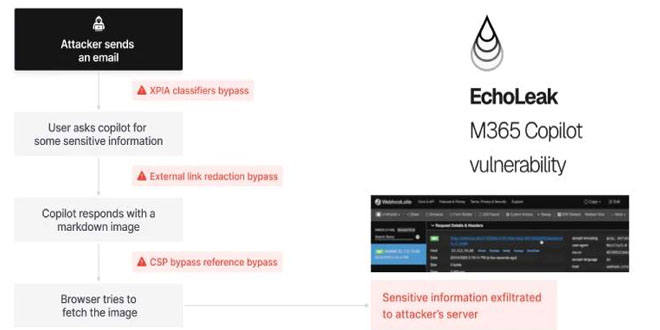
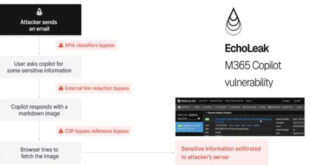
Microsoft’s June Patch Tuesday update has arrived, addressing 66 vulnerabilities across its product line. One of these flaws was actively being exploited, making this update crucial for both businesses and individual users.
One Zero-Day Actively Exploited:
The important fix addresses CVE-2025-33053, a vulnerability in Windows WebDAV that could let attackers execute code remotely. This flaw was already being exploited before today’s patch, making it a “zero-day”.
The WebDAV flaw affects Windows 10, Windows 11, and related server versions. Microsoft has acknowledged its active exploitation but hasn’t provided complete information.
10 Critical Issues Fixed:
Along with a zero-day vulnerability, Microsoft resolved 10 Critical issues that can lead to remote code execution or privilege escalation with little user interaction. Four of these vulnerabilities are in Microsoft Office, which is often targeted by attackers sending malicious emails.
Fixes are being issued for Microsoft Edge, Power Automate, .NET, and parts of Windows. None were reported as actively exploited, but some could be targeted soon.
Windows Update Details:
The updated packages are available now and include:
Windows 11: KB5060842 (22H2 and 23H2)
Windows 10: KB5060533 and KB5060999
Windows Server versions: Also updated, depending on the build in use.
Admins must check their update systems to confirm successful rollouts and identify any compatibility problems with the latest patches.
What to Do Now:
Apply all available June updates as soon as possible, especially for systems using WebDAV
Review your Office file handling policies, especially if users frequently receive documents from outside the organization
Monitor network traffic for signs of suspicious activity linked to WebDAV or other patched services
Test in staging environments before rolling out company-wide, especially in environments with older or customized software stacks
The complete advisory from Microsoft is in its security update guide. Quickly applying patches helps defend against numerous cyberattacks.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind