A recent Bitdefender report reveals that Medusa is still actively attacking and has created a notable presence on both the dark web and surface web, making it a ransomware group to monitor.
Medusa stands out from other ransomware groups by maintaining a name-and-shame blog on the surface web, where it shares details about its victims in addition to using dark web leak sites. They actively engage on social media platforms like X (formerly Twitter) and Telegram to provide updates on their attacks, enhancing their visibility. Their association with an entity named “OSINT Without Borders” is also uncommon for ransomware operators.
Medusa is a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) platform that lets affiliates, usually independent hackers, launch attacks and share the ransom profits. Affiliates keep most of the ransom, while Medusa takes a smaller share. This model has allowed Medusa to quickly expand its attacks across various sectors, including healthcare, manufacturing, education, finance, and government worldwide.
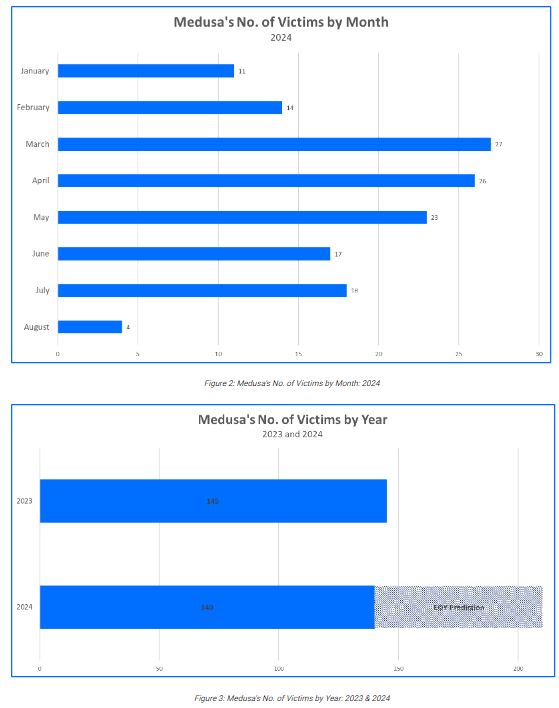
Since 2023, the Medusa ransomware group has targeted more victims, with estimates suggesting over 200 organizations could be affected in 2024, up from 145 in 2023. Their attacks have impacted companies worldwide, including in the United States, Israel, England, and Australia.
Medusa’s activities extend beyond ransomware. They are connected to an OSINT platform called “OSINT Without Borders,” which shares information on data breaches and hacker activities. Although Medusa claims OSINT Without Borders is independent, cybersecurity analysts found links, such as shared Telegram channels and similar content. This suggests a complex strategy for intelligence gathering and public relations.
The site operated by “OSINT Without Borders” includes disclaimers against illegal activity, yet it often mentions Medusa’s actions. This confusion between OSINT and ransomware makes Medusa a particularly risky and unpredictable threat.
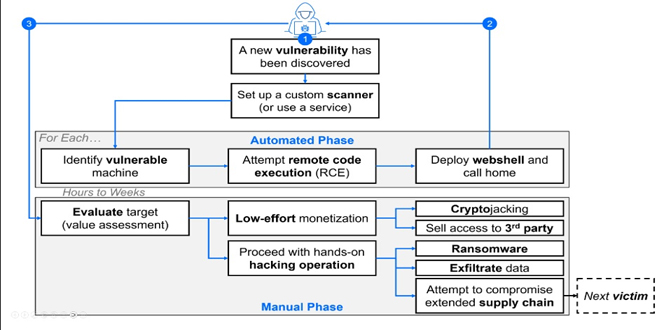
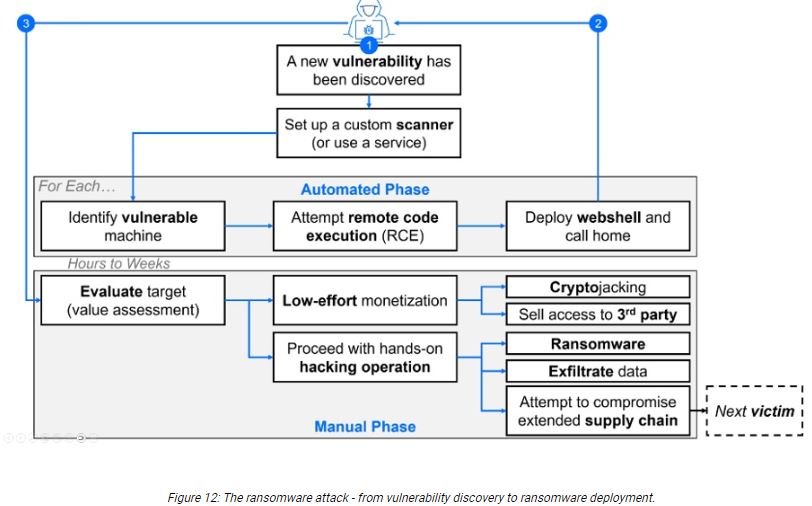
According to the report published by Bitdefender, “Medusa gains access to a target system through a known weakness such as the Fortinet EMS SQL injection vulnerability. CVE-2023-48788 impacts environments that have FortiClient EMS, versions 7.2 to 7.2.2 and 7.0.1 to 7.0.10, installed to manage endpoints.
The vulnerability allows the attacker to send malicious web requests containing SQL statements. The malicious SQL input is designed to alter the FCTUID parameter that is found in the header section of requests and passed to Fortinet’s FCTDas service. FCTDas is a program that interprets incoming requests that are routed to the SQL server database.
After the FCTUID parameter falls victim to the SQL injection process, allowing the attacker to manipulate application queries, the attacker passes SQL input to issue the xp_cmdshell command. xp_cmdshell is a native component of Microsoft’s SQL Server. When the command is invoked, the attacker performs remote code execution, issuing commands that impact the affected server and connected resources and hosts. Medusa creates a webshell on the exploited server to exchange payloads and host data. This is accomplished using a service such as bitsadmin. The webshell is configured to encrypt and/or conceal traffic.”
Organizations should proactively patch known vulnerabilities, especially in remote management systems and SQL injection flaws, to defend against Medusa’s attacks. Additionally, monitoring suspicious network activity related to third-party tools like ConnectWise, AnyDesk, and bitsadmin can help detect compromises early.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind