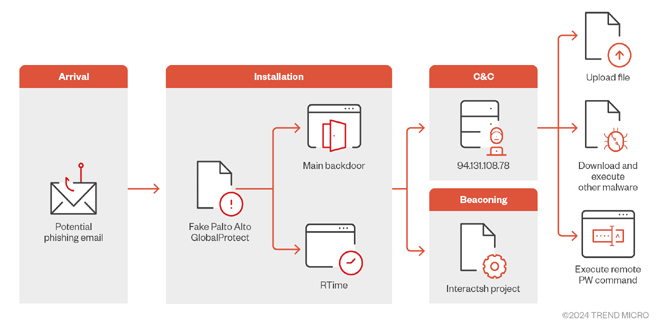
Trend Micro researchers identified a sophisticated malware campaign that aims at Middle East organizations. The campaign tricks victims into infecting their devices by pretending to be a real Palo Alto GlobalProtect VPN client.
The attack begins with the distribution of a malicious file named “setup.exe,” which masquerades as a legitimate installation package for Palo Alto Networks’ GlobalProtect VPN. Once executed, this file deploys “GlobalProtect.exe” along with configuration files “RTime.conf” and “ApProcessId.conf” into the victim’s system directory, specifically within the path C:\Users\ UserName)\AppData\Local\Programs\PaloAlto\.
The malware deceives by using a command-and-control infrastructure with a new URL named “sharjahconnect.” The URL is designed to look like a legitimate company VPN portal, helping the malware to infiltrate and maintain access to compromised networks without being detected.
A particularly notable aspect of this malware is its use of the Interactsh project, a tool typically used by penetration testers to verify exploit success, for beaconing purposes. By leveraging Interactsh, the malware sends DNS requests to domains within the oast[.]fun domain, such as step[1-6]-{dsktoProcessId}.tdyfbwxngpmixjiqtjjote3k9qwc31dsx.oast.fun. These beaconing requests correspond to various stages of the infection process, from collecting machine information to executing commands received from the C&C server.
This method helps threat actors track their malware’s progress as it spreads, giving them real-time information about which targets have been compromised.
This malware, created in C#, can perform remote PowerShell commands, download and run more payloads, and steal specific files from the infected machine. Its command structure is flexible, enabling it to carry out various tasks.
Executing PowerShell Scripts:
The malware can run PowerShell commands and send the results back to the C&C server.
Process Management:
It can start new processes, download files from a specified URL, and upload stolen files to a remote server.
Data Encryption:
To secure its communications, the malware employs AES encryption, ensuring that data sent to the C&C server is protected from interception.
These capabilities make the malware a powerful tool for spying and stealing data, with the potential to cause serious harm to targeted organizations.
The malware uses smart techniques to avoid being detected by security tools. It checks file paths and specific files before running its main code, making it hard to find in controlled analysis environments. It also uses newly registered domains for its activities, which makes it difficult to detect and attribute the attack to a specific threat actor.
Companies in the Middle East and around the world need to stay alert and take action to improve their defenses against these threats. This means using strong endpoint protection, keeping security protocols up to date, and focusing on educating and raising awareness among employees.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind