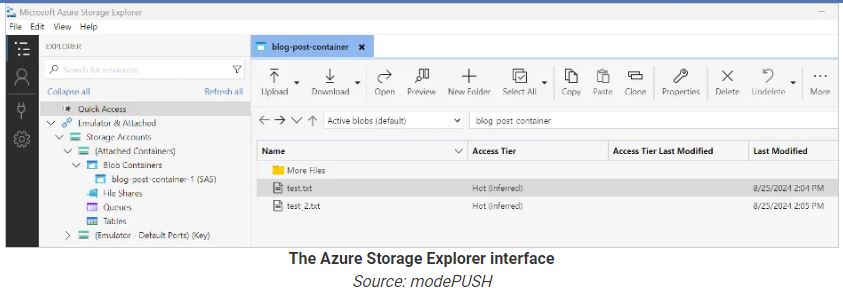
Ransomware groups like BianLian and Rhysida use Microsoft’s Azure Storage Explorer and AzCopy to steal data from hacked networks and store it in Azure Blob storage. Storage Explorer is a GUI tool for managing Microsoft Azure, while AzCopy is a command-line tool for large data transfers to and from Azure storage.
Cybersecurity firm modePUSH has seen attacks where stolen data is stored in an Azure Blob container in the cloud, allowing threat actors to transfer it to their own storage later.
However, the researchers noted that the attackers had to put in extra work to get Azure Storage Explorer working, including installing dependencies and upgrading .NET to version 8.
Ransomware gangs often use Rclone to sync files with different cloud providers and MEGAsync for syncing with MEGA cloud, despite having their own tools.
Azure is a trusted enterprise service, so it’s unlikely to be blocked by corporate firewalls. Consequently, data transfers through it are more likely to succeed unnoticed.
Azure’s scalability and performance are advantageous for managing large amounts of unstructured data, especially when attackers try to quickly exfiltrate many files.
modePUSH observed ransomware actors using several instances of Azure Storage Explorer to quickly upload files to a blob container.
Detecting ransomware exfiltration:
The researchers discovered that the attackers turned on basic logging when using Storage Explorer and AzCopy, which generates a log file at %USERPROFILE%\.azcopy.
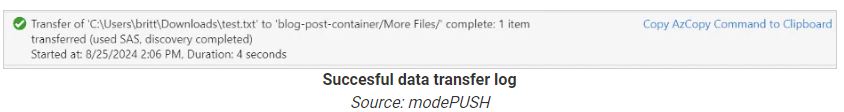
This log file is valuable for incident responders because it shows file operations, helping investigators quickly identify stolen data (UPLOADSUCCESSFUL) and possible introduced payloads (DOWNLOADSUCCESSFUL).
Defense measures involve monitoring AzCopy execution, tracking outbound traffic to Azure Blob Storage at “.blob.core.windows.net” or Azure IP ranges, and setting alarms for unusual file access or copying patterns on critical servers.
If your organization uses Azure, enable the ‘Logout on Exit’ option to automatically sign out when exiting the application, preventing unauthorized access to the active session.
(Source: modePUSH, Bleepingcomputer)
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind