Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs (CRIL), CRIL has uncovered a Go Stealer possibly targeting the Indian Air Force. This malware is propagated through a ZIP file named “SU-30_Aircraft_Procurement”. The ZIP file is hosted on Oshi (hxxps://oshi[.]at/ougg), an anonymous file storage platform and the Threat Actor (TA) could potentially be distributing this link via spam email or similar channels.
In September 2023, the Indian defense ministry approved a project to acquire 12 Su-30 MKI fighter jets. The Threat Actor (TA) seems to be leveraging this notification as a means to create bait to target professionals within the Indian Air Force.
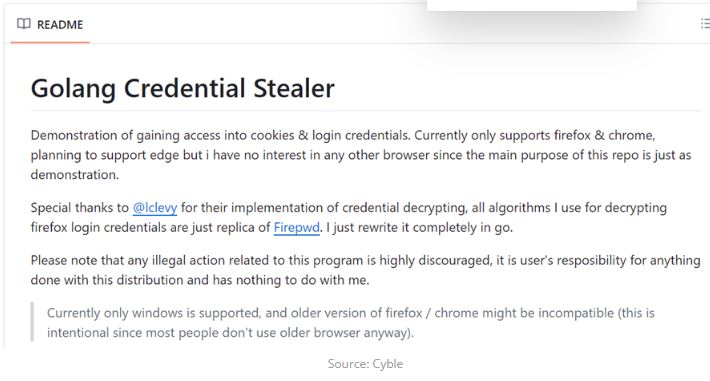
The record reported that the delivered malware is a variant of a Go Stealer, based on open-source malware found on GitHub. It has added features, such as targeting different web browsers and stealing data through Slack.
Using Slack for secret communication exploits its prevalence in business networks, allowing malicious activities to hide within normal traffic.
The attacks were probably intentional because this stealer is designed to steal login credentials and cookies from web browsers.
“The targeted nature of this malware suggests a tactical approach aimed at acquiring specific sensitive information from the infected systems,” researchers said.
Cyble couldn’t attribute this campaign to a specific threat actor “due to the limited information available at the moment.” The Indian Air Force hasn’t responded to a request for comment.
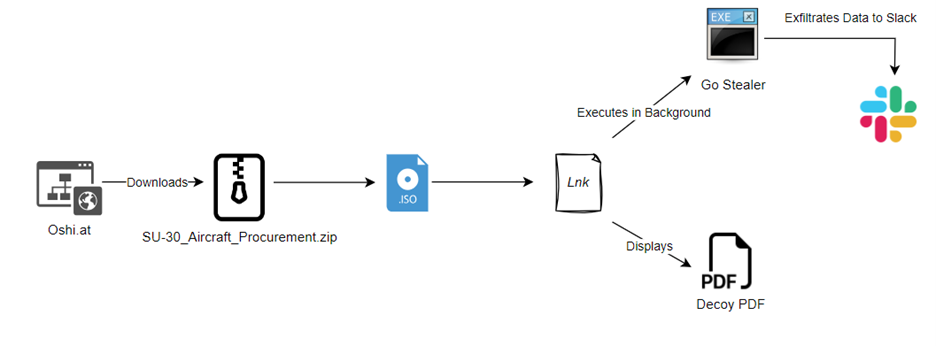
The Threat Actor (TA) behind this attack is currently unknown due to the limited availability of information. The attack unfolds in a sequence involving a ZIP file, an .iso file, a .lnk file, and, ultimately, the deployment of the stealer payload. The figure below shows the infection chain.
“The hackers appear to be exploiting this event to target Indian Air Force professionals,” researchers at the cybersecurity firm Cyble said.
Technical Analysis of the Go Stealer:
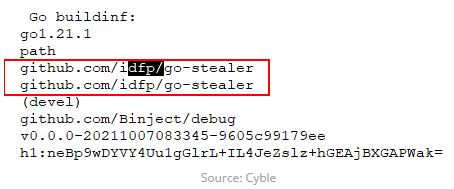
The new Go Stealer variant has more advanced features than the one on GitHub. It is coded in Go programming language and is based on an open-source Go Stealer from GitHub. This variant has new features such as wider browser targeting and a new way to send stolen data through Slack.
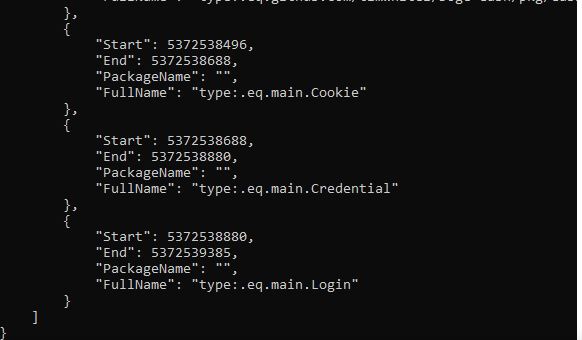
The stealer creates a log file in the victim’s system when executed. It uses GoLang tools like GoReSym to analyze the system in detail.

The malware is carefully designed to collect login credentials and cookies from specific internet browsers: Google Chrome, Edge, and Brave.
(Media Disclaimer: This report summarizes both internal and external sources, gathered through various methods. The information provided is for reference only, and users are solely responsible for relying on it. Infosecbulletin does not accept responsibility for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.)
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind














