Today, CISA ordered federal agencies to patch recently patched security vulnerabilities exploited as zero-days to deploy Triangulation spyware on iPhones via iMessage zero-click exploits.
The warning comes after Kaspersky published a report detailing a Triangulation malware component used in a campaign it tracks as “Operation Triangulation.”
Kaspersky says it found the spyware on iPhones belonging to employees in its Moscow office and from other countries. The attacks started in 2019 and are still ongoing, according to the company, and they use iMessage zero-click exploits that exploit the now-patched iOS zero-day bugs.
ALSO READ:
Critical vulnerability in Fortinet FortiNAC, allow attackers taking control of systems
Russia’s FSB intelligence agency also claimed that Apple collaborated with the NSA to create a backdoor, facilitating the infiltration of iPhones in Russia. The FSB also said it allegedly found thousands of infected iPhones owned by Russian government officials and embassy staff in Israel, China, and NATO member nations.
“We have never worked with any government to insert a backdoor into any Apple product and never will,” an Apple spokesperson told BleepingComputer.
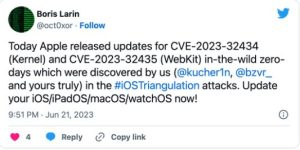
“Apple is aware of a report that this issue may have been actively exploited against versions of iOS released before iOS 15.7,” the company said on Wednesday when describing the two Kernel and WebKit vulnerabilities (CVE-2023-32434 and CVE-2023-32435) exploited in the attacks.
The company also fixed a WebKit zero-day (CVE-2023-32439) this week that can let attackers gain arbitrary code execution on unpatched devices. This was also tagged by CISA today as an actively exploited flaw.
The list of affected devices is extensive, as the zero-day affects older and newer models, and it includes:
iPhone 8 and later, iPad Pro (all models), iPad Air 3rd generation and later, iPad 5th generation and later, iPad mini 5th generation and later
iPhone 6s (all models), iPhone 7 (all models), iPhone SE (1st generation), iPad Air 2, iPad mini (4th generation), and iPod touch (7th generation)
Macs running macOS Big Sur, Monterey, and Ventura
Apple Watch Series 4 and later, Apple Watch Series 3, Series 4, Series 5, Series 6, Series 7, and SE
On Thursday, Apple sent another round of threat notifications alerting customers they were targeted in state-sponsored attacks, one day after patching the zero-days exploited to deploy Triangulation spyware. However, it’s not clear to what incidents these new warnings are related to, according to CNN reporter Chris Bing.
Federal agencies ordered to patch by July 14th
Another vulnerability CISA added to its known exploited vulnerabilities (KEV) list today is a critical pre-authentication command injection bug (CVE-2023-27992) that can let unauthenticated attackers execute operating system commands on Internet-exposed Network-Attached Storage (NAS) devices left unpatched.
Zyxel warned customers on Tuesday to secure their NAS devices “for optimal protection,” weeks after Mirai-based botnets targeted Zyxel firewalls and VPN products in a massive wave of attacks.
CISA also included a VMware ESXi vulnerability (CVE-2023-20867) in its KEV catalog. This bug was abused by a Chinese-backed hacking group (UNC3886) to backdoor Windows and Linux virtual machines in data theft attacks.
U.S. Federal Civilian Executive Branch Agencies (FCEB) must patch all security vulnerabilities added to CISA’s KEV catalog within an allotted timeframe, according to a binding operational directive (BOD 22-01) released in November 2022.
After the latest update, federal agencies have been instructed to secure vulnerable devices against flaws included today by June 14th, 2023.
While BOD 22-01 primarily focuses on U.S. federal agencies, it is strongly recommended that private companies also prioritize addressing the vulnerabilities outlined in CISA’s KEV list, which includes bugs known to be exploited in attacks.
Source: Bleeping computer
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind