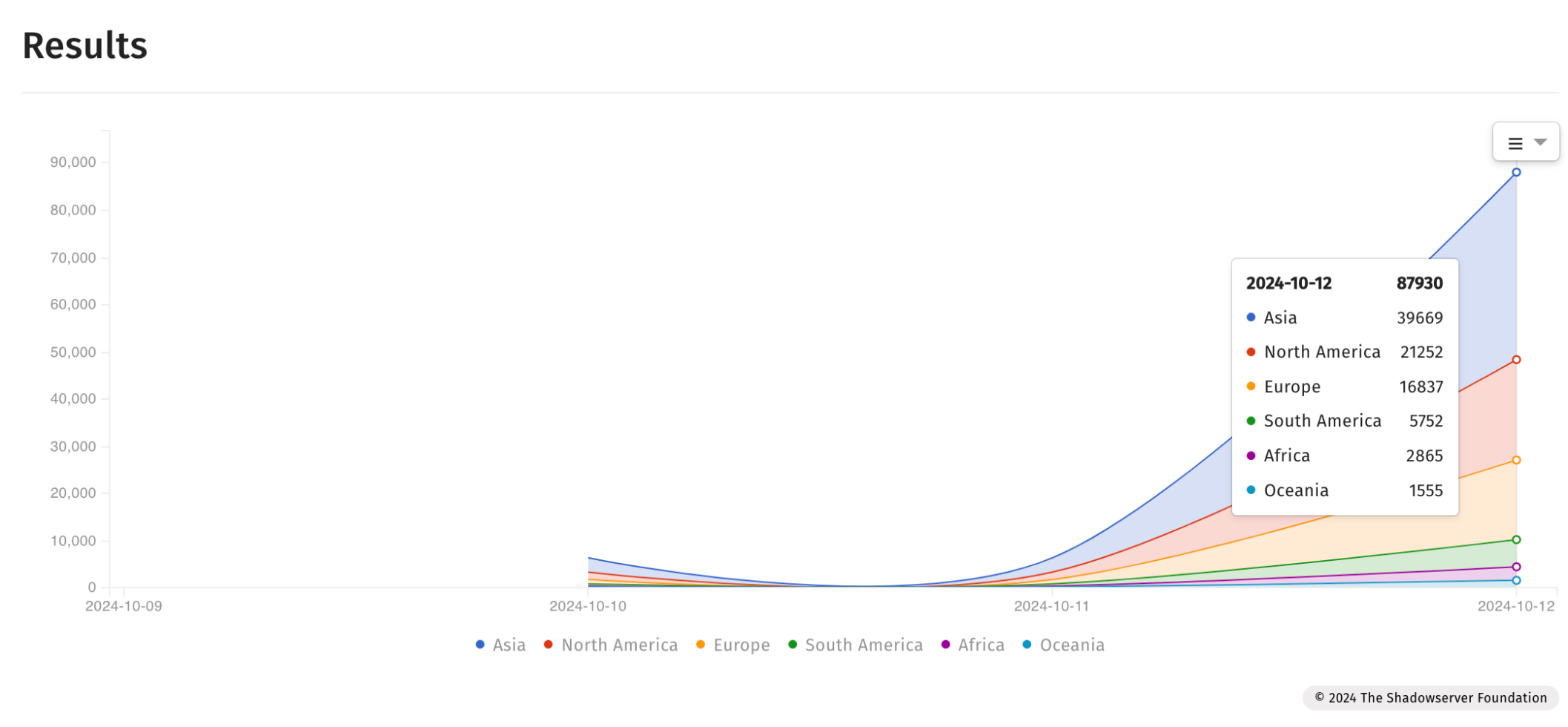
On Sunday, the Shadowserver Foundation revealed that over 87,000 internet-facing Fortinet devices may still be at risk due to (CVE-2024-23113) vulnerability.
About CVE-2024-23113:
CVE-2024-23113, a format string vulnerability that affects the FortiOS FGFM (FortiGate to FortiManager) daemon and can be triggered via specially crafted requests, was discovered and reported by Gwendal Guégniaud of Fortinet Product Security team and patched in early February 2024 in FortiOS versions 7.4.3, 7.2.7 and 7.0.14.
Since then, Fortinet has updated its advisory to list more affected products and provide a mitigation measure that includes removing FGFM access.
“Note that this will prevent FortiGate discovery from FortiManager [a solution for managing Fortinet products]. Connection will still be possible from FortiGate,” the company warned.
“Please also note that a local-in policy that only allows FGFM connections from a specific IP will reduce the attack surface but it won’t prevent the vulnerability from being exploited from this IP. As a consequence, this should be used as a mitigation and not as a complete workaround.”
On Monday, watchTowr Labs released their findings about the vulnerability and described the challenges they faced when using a testing tool they developed, as different firmware versions responded differently to their attempts to probe.
“It looks like Fortinet added some kind of certificate validation logic in the 7.4 series, meaning that we can’t even connect to it (let alone send our payload) without being explicitly permitted by a device administrator. We also checked the 7.0 branch, and here we found things even more interesting, as an unpatched instance would allow us to connect with a self-signed certificate, while a patched machine requires a certificate signed by a configured CA,” watchTowr Labs researcher Aliz Hammond explained.
“We did some reversing and determined that the certificate must be explicitly configured by the administrator of the device, which limits exploitation of these machines to the managing FortiManager instance (which already has superuser permissions on the device) or the other component of a high-availability pair.”
The status of whether the vulnerability is being used in ransomware attacks remains “unknown,” as it was last week.
The CVSS v3 severity rating for CVE-2024-23113 is 9.8, indicating a critical remote code execution vulnerability. Exploiting it would severely impact data confidentiality, system integrity, and service availability, requiring no privileges or user interaction.
Administrators should upgrade to unaffected versions of FortiOS, FortiPAM, FortiProxy, and FortiWeb, or follow the mitigation measures in Fortinet’s advisory.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind














