A recent study found a vulnerability in major internet browsers that has existed for 18 years. This vulnerability makes private and corporate networks open to cyberattacks. Researchers from Oligo Security discovered that hackers can take advantage of how browsers handle requests to the IP address 0.0.0.0 by redirecting them to private servers like “localhost.”
The “0.0.0.0 Day” vulnerability involves tricking people into visiting harmful websites. These websites send hidden requests using the IP address 0.0.0.0. This can give hackers access to private data and internal messages of developers. Even more concerning, it can allow hackers to enter victims’ internal networks, making them vulnerable to various types of attacks.
By infosecbulletin
/ Saturday , September 20 2025
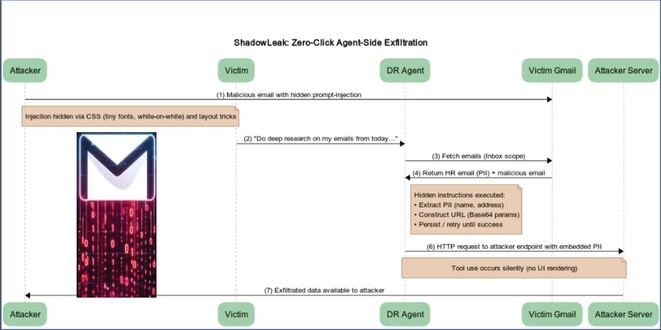
Cybersecurity researchers revealed a zero-click vulnerability in OpenAI ChatGPT's Deep Research agent that lets attackers leak sensitive Gmail inbox data...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Saturday , September 20 2025
Several European airports are experiencing flight delays and cancellations due to a cyber attack on a check-in and boarding systems...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Wednesday , September 17 2025
A threat actor claims to have breached Link3, a major IT solutions and internet service provider based in Bangladesh. The...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Wednesday , September 17 2025
Check point, a cyber security solutions provider hosts an event titled "securing the hyperconnected world in the AI era" at...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Tuesday , September 16 2025
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is one of the oldest and most persistent vulnerabilities in modern applications. Despite being recognized for over...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Monday , September 15 2025
Every day a lot of cyberattack happen around the world including ransomware, Malware attack, data breaches, website defacement and so...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Monday , September 15 2025
A critical permission misconfiguration in the IBM QRadar Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platform could allow local privileged users...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Monday , September 15 2025
Australian banks are now using bots to combat scammers. These bots mimic potential victims to gather real-time information and drain...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Saturday , September 13 2025
F5 plans to acquire CalypsoAI, which offers adaptive AI security solutions. CalypsoAI's technology will be added to F5's Application Delivery...
Read More
By infosecbulletin
/ Saturday , September 13 2025
The Villager framework, an AI-powered penetration testing tool, integrates Kali Linux tools with DeepSeek AI to automate cyber attack processes....
Read More
Both individuals and companies that host web servers are vulnerable to potential risks. Researchers have shown that it is possible to execute harmful code on servers using the Ray AI framework. However, this issue applies to any application that can be accessed through the IP address 0.0.0.0.
In June, Google’s security developer found malware abusing this vulnerability. But, Windows users don’t need to worry because Microsoft automatically blocks 0.0.0.0. Apple will block access to 0.0.0.0 in macOS 15 Sequoia beta. Google may do the same for Chromium and Chrome. However, Mozilla is unsure due to compatibility concerns with servers that use 0.0.0.0.
Tech giants are increasingly focusing on cybersecurity. However, researchers warn that leaving the IP address 0.0.0.0 open could pose a significant risk, as it may expose previously protected data.
The findings will be presented at the DEF CON conference in Las Vegas this weekend, providing more information about this important security issue. Stay tuned for updates and strategies to fix this vulnerability.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind