OpenAI has neutralized over 20 malicious cyber operations using its AI chatbot, ChatGPT, for creating malware, spreading misinformation, avoiding detection, and spear-phishing.
The report confirms that since the start of the year, generative AI tools are being used to improve offensive cyber operations. OpenAI’s latest report reveals that Chinese and Iranian threat actors are misusing ChatGPT to improve their operations.
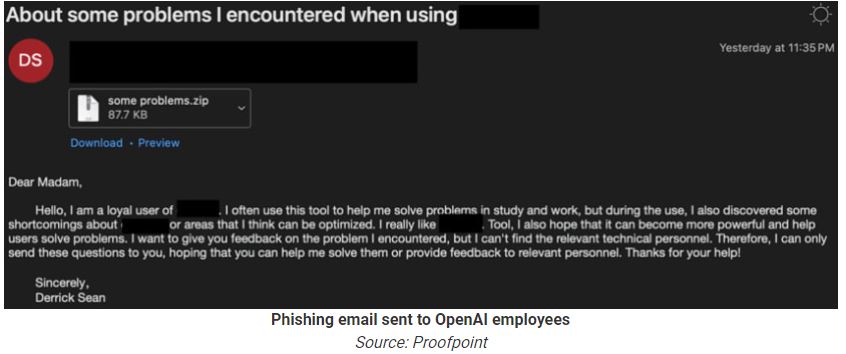
A Chinese threat group named “SweetSpecter” tried to use ChatGPT for research and malware creation. They also attempted spear-phishing attacks on OpenAI employees. Opening the attachments initiated an infection that installed the SugarGh0st RAT on the victim’s system.
The Iranian group “CyberAv3ngers,” linked to the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, posed a serious threat by using ChatGPT to find weaknesses in industrial control systems and create attack scripts for critical infrastructure.
OpenAI reports that a threat group requested ChatGPT to generate default credentials for popular Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), create custom bash and Python scripts, and obfuscate code.
Iranian hackers used ChatGPT to plan their actions after compromising systems, learn to exploit vulnerabilities, and decide how to steal user passwords on macOS.
The third case in OpenAI’s report focuses on Storm-0817, a group of Iranian threat actors. The group allegedly used ChatGPT for various tasks, including debugging malware, creating an Instagram scraper, translating LinkedIn profiles into Persian, and developing custom Android malware with the necessary command and control infrastructure.
Malware developed using OpenAI’s chatbot can steal contact lists, call logs, files, take screenshots, access browsing history, and determine the user’s location.
“In parallel, STORM-0817 used ChatGPT to support the development of server side code necessary to handle connections from compromised devices,” reads the Open AI report.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind