A new class of vulnerabilities in Intel processors, called Branch Predictor Race Conditions (BPRC), enables attackers to extract sensitive data from the cache and RAM of other users on the same hardware.
Recent research by computer scientists from the Computer Security Group (COMSEC) at the Department of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at ETH Zurich shows the vulnerabilities that can be exploited to misuse the prediction calculations of the CPU (central processing unit) in order to gain unauthorised access to information from other processor users.
Kaveh Razavi, head of COMSEC said, “The security vulnerability affects all Intel processors,”. “We can use the vulnerability to read the entire contents of the processor’s buffer memory (cache) and the working memory (RAM) of another user of the same CPU.” The CPU uses the RAM (random access memory) and cache to temporarily store calculation steps and information that is likely to be needed next.
This vulnerability threatens data security, especially in cloud environments where users share hardware. It impacts the processors from the largest CPU manufacturer, used in PCs, laptops, and data center servers.
Nanosecond gap in authority check:
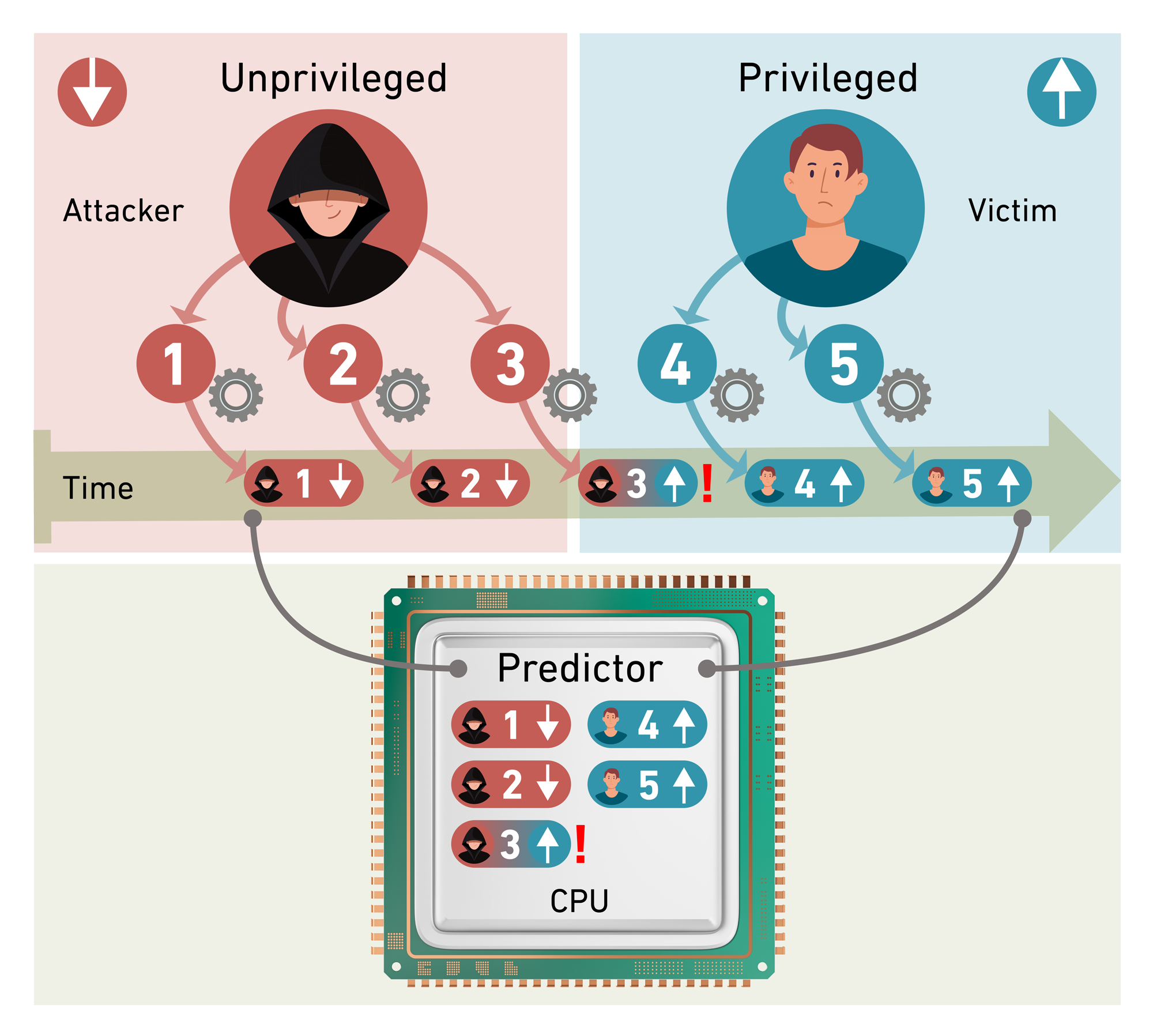
Sandro Rüegge examining the vulnerability in detail over the past few months said,”The so-called BPRC (Branch Predictor Race Conditions) emerge during a brief period of a few nanoseconds when the processor switches between prediction calculations for two users with different permissions.”
An attacker can exploit vulnerabilities in user privileges because permissions for actions are not stored simultaneously with calculations. By manipulating inputs, they can create confusion when switching users, leading to incorrect privilege assignments. This could allow them to read an information byte, which is made up of eight binary bits.
Unlocking entire contents of memory byte by byte:
Disclosing a single byte is minor, but the attack can be quickly repeated, allowing the entire memory to be read gradually, according to Rüegge. “We can trigger the error repeatedly to read over 5000 bytes per second.” Thus, during an attack, it’s only a matter of time before all CPU memory is compromised.
Part of a series of security vulnerabilities:
ETH Zurich researchers have identified a new vulnerability in speculative CPU technologies, which dates back to the mid-1990s. The first major vulnerabilities, Spectre and Meltdown, emerged in 2017, followed by various new variants. In 2022, former PhD student Johannes Wikner discovered Retbleed, which exploited speculatively executed instructions in the CPU’s cache to access other users’ information.
Suspicious signal reveals vulnerability:
Johannes Wikner said, “The starting point for the discovery of the new vulnerability class was work that followed on from the Retbleed investigations. “I examined the functions of the protective measures that Intel had introduced to patch up the Retbleed vulnerability.”
In doing so, he discovered an unusual signal from the cache memory that appeared regardless of whether the protective measures were enabled or disabled. Rüegge then took over detailed analysis of the cause of the signal and, based on this work, was able to uncover the new attack vector.
Fundamental architectural problem:
The vulnerability was discovered back in September 2024. Since then, Intel has put measures in place to protect its processors. However, it appears that the issue is more severe. “The series of newly discovered vulnerabilities in speculative technologies shows that there are basic flaws in the architecture,” Razavi points out. “We need to identify each gap and fix them.”
This requires a specific update to the processor’s microcode, which can be installed through a BIOS or operating system update that should be included in one of the latest cumulative updates from Windows.
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind