Bangladesh Cyber Threat Landscape 2024, by BGD e-GOV CIRT, reveals a sharp escalation in cyber threats across Bangladesh. The year saw a surge in ransomware, phishing, hacktivism, and data breaches, affecting both public and private sectors. Critical vulnerabilities in outdated systems, increased use of the dark web for trading stolen data, and the emergence of new ransomware groups demonstrate the evolving sophistication of adversaries. This report outlines key findings, trends, and sectoral impacts to provide a comprehensive understanding of the nation’s cyber risk environment.
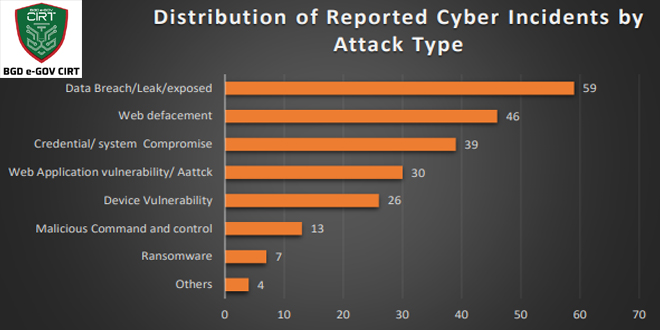
Incident Statistics:
In 2024, BGD e-GOV CIRT issued 188 cybersecurity reports, including alerts, advisories, and investigation findings. The most common incident types includeing, Data breaches and leaks from IT and financial service providers, Web defacements targeting universities and government institutions, Credential and system compromises through phishing and malware, Ransomware attacks, which more than doubled compared to 2023.
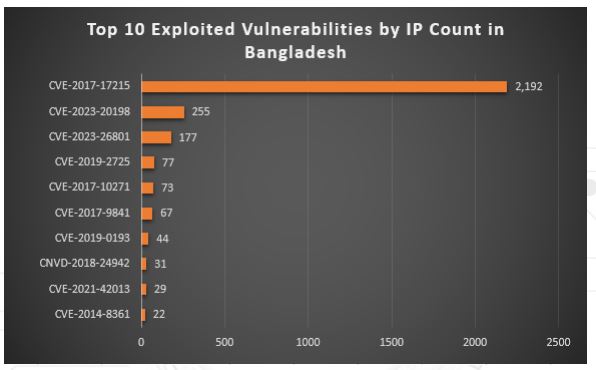
Exploited Vulnerabilities:
In 2024, a total of 602 software vulnerabilities were actively exploited in Bangladesh, affecting an average of 905 IP addresses per day. The most prevalent was CVE-2017-17215, a critical flaw in Huawei routers, which left 2,192 systems exposed to attackers. Alongside this, high-severity vulnerabilities such as CVE-2023-20198 in Cisco IOS XE and long-standing weaknesses in Oracle WebLogic continued to be heavily targeted. Alarmingly, several legacy flaws dating back to 2014 remain unpatched across national infrastructure, underscoring persistent gaps in patch management and vulnerability remediation.
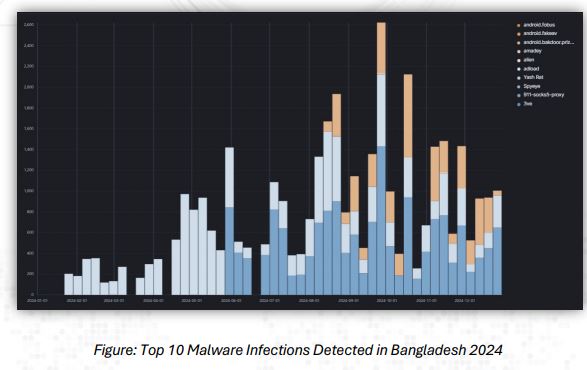
Malware Trends:
In 2024, nearly 24,000 Bangladeshi IP addresses were identified as infected with various forms of malware. The most widespread families included Emotet, Mirai, Qakbot, Trickbot, alongside several Remote Access Trojans (RATs) such as Remcos and NetWire. The prominence of Mirai variants highlighted the growing risks posed by insecure Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which remain attractive targets for large-scale botnet operations. Meanwhile, RATs and banking Trojans were leveraged extensively for credential theft and financial fraud, posing significant risks to both individuals and organizations.
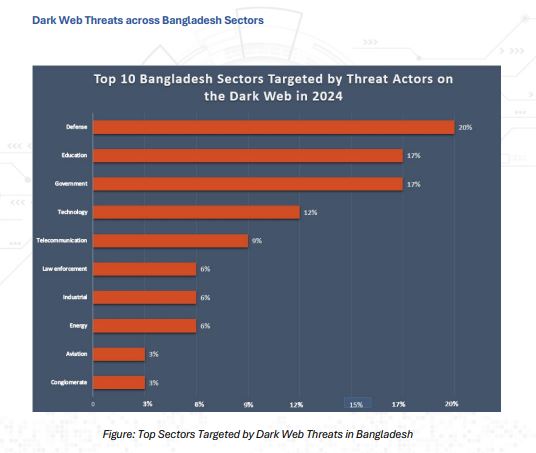
Dark Web Threats
In 2024, dark web forums emerged as a central hub for malicious activity in Bangladesh, serving as marketplaces for data sales, platforms for extortion, and channels for spreading misinformation. Several high-profile incidents underscored this trend: in May, millions of personally identifiable records were leaked from a local IT service provider; in October, root access to a critical server belonging to an energy company was openly advertised for sale; and in November, the data of over 10 million mobile financial service (MFS) users—including phone numbers and SMS transaction records—was leaked. Analysis revealed that the most frequently compromised data types included email addresses, full names, and phone numbers, followed by sensitive identifiers such as government-issued IDs and financial information. The sectors most heavily targeted were defense, education, government, and telecommunications, highlighting the broad spectrum of risks facing Bangladesh’s critical infrastructure and services.
Hacktivism and Disruption
Hacktivist activity in Bangladesh intensified throughout 2024, with a noticeable shift in focus toward the education sector. Universities and schools became prime targets for defacement attacks, often carried out by exploiting weak administrator credentials and outdated web applications. At the same time, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks surged, peaking at an unprecedented 15.64 Tbit/sec in December, disrupting critical online services. Hacktivists also engaged in website scraping campaigns, harvesting publicly accessible data from educational and government institutions, later distributing it on dark web forums and messaging platforms. Notably, Bangladeshi hacktivist groups moved away from cross-border cyber conflicts and increasingly directed their efforts toward domestic political protests, using cyberattacks as a tool of dissent against national policies.
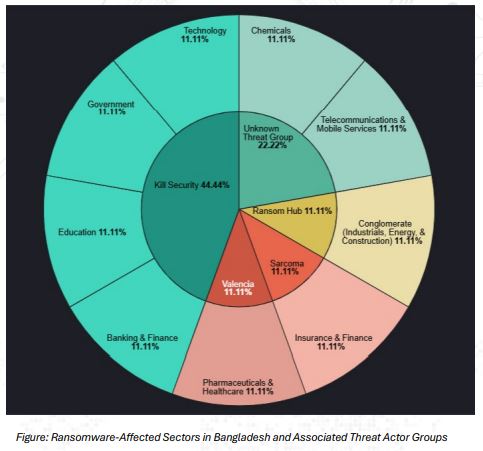
Ransomware Landscape:
Ransomware remained the most severe cyber threat to Bangladesh in 2024, with activity increasing by an alarming 125% compared to the previous year. While long-established groups such as LockBit and ALPHV/BlackCat continued to operate, a wave of emerging actors—notably Kill Security, Valencia, RansomHub, and Sarcoma—rose to prominence and overtook traditional players in terms of impact. Several high-profile incidents marked this trend: Kill Security leaked confidential government documents; Valencia crippled a pharmaceutical company and exposed sensitive financial and operational records; RansomHub targeted a large conglomerate, threatening to release 350GB of stolen data unless ransom demands were met; and Sarcoma compromised an insurance provider, stealing 36GB of data and employing aggressive extortion tactics. These cases reflect broader shifts in the ransomware ecosystem, characterized by the growth of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), widespread adoption of Living-off-the-Land (LoTL) techniques to evade detection, and increasingly common double-extortion strategies that combine encryption with threats of public data exposure.
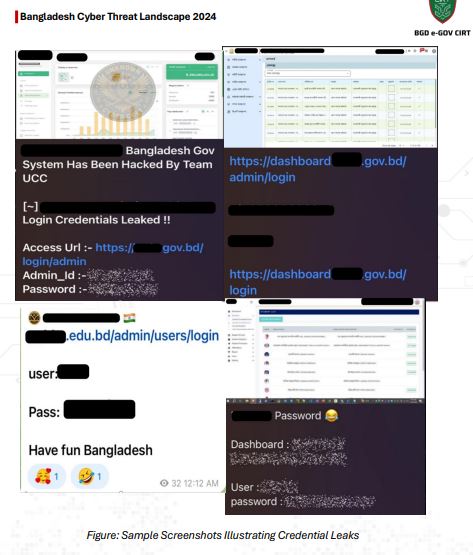
Phishing and Credential Theft:
Phishing remained one of the most effective attack vectors, with government and law enforcement bodies being prime targets. Attackers spoofed .gov.bd domains and leveraged free hosting platforms like Netlify to create fake login pages. Malicious attachments (.rar, .pdf, .html, and disguised executables) were used to deliver malware payloads. Credential-stealing malware families such as Lumma, Redline, Raccoon, Stealc, Meta, and Taurus harvested login data and sold them on the dark web.
In 2024, the cyber threat landscape in Bangladesh was marked by increasingly sophisticated threat actors. The primary threats were driven by ransomware, hacktivism, phishing, and activity on the dark web. Attacks were largely enabled by social engineering, unpatched vulnerabilities, and poor cyber hygiene practices.
“SikkahBot” Malware targets “bKash” “Nagad” “MYGP” “DBBL” with banking users in Bangladesh
 InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind
InfoSecBulletin Cybersecurity for mankind